Tenure experience demonstrates long-term commitment and in-depth knowledge acquired through years of consistent work, providing a solid foundation for positions requiring stability and proven expertise. Micro-credential experience offers targeted, up-to-date skills and specialized knowledge that can quickly adapt to evolving industry demands and technologies. Combining both types of experience enhances a candidate's versatility and ability to meet varied job requirements effectively.
Table of Comparison
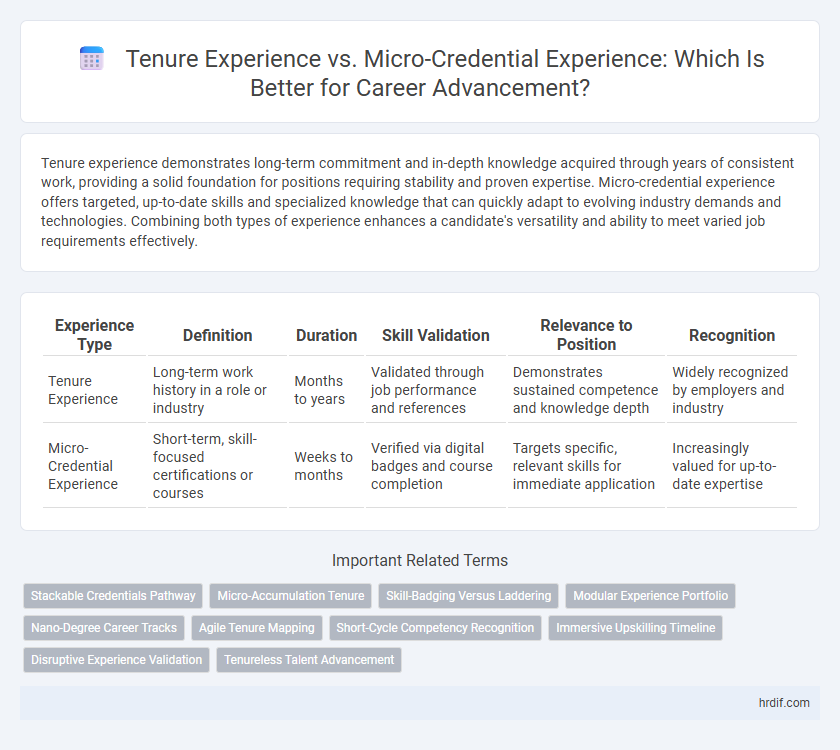
| Experience Type | Definition | Duration | Skill Validation | Relevance to Position | Recognition |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tenure Experience | Long-term work history in a role or industry | Months to years | Validated through job performance and references | Demonstrates sustained competence and knowledge depth | Widely recognized by employers and industry |
| Micro-Credential Experience | Short-term, skill-focused certifications or courses | Weeks to months | Verified via digital badges and course completion | Targets specific, relevant skills for immediate application | Increasingly valued for up-to-date expertise |
Defining Tenure Experience and Micro-Credential Experience
Tenure experience refers to long-term, continuous employment in a specific role or organization, demonstrating sustained expertise and commitment. Micro-credential experience encompasses short-term, specialized training achievements that validate specific skills or knowledge, often through digital badges or certificates. Both forms of experience contribute uniquely to professional qualifications, with tenure highlighting depth and reliability, while micro-credentials showcase current and targeted competencies.
The Value of Longevity: What Tenure Offers Employers
Tenure experience provides employers with proven reliability, deep organizational knowledge, and a track record of sustained performance that micro-credential experience alone may not demonstrate. Long-term employees contribute to company culture stability, mentorship, and institutional memory critical for strategic decision-making and consistent productivity. While micro-credentials offer specialized skills, tenure embodies commitment and adaptability within the evolving workplace environment, enhancing overall employer confidence.
Micro-Credentials: Fast-Tracking Skill Acquisition
Micro-credential experience accelerates skill acquisition by providing targeted, industry-relevant competencies that can be immediately applied in professional settings, unlike traditional tenure experience which often emphasizes prolonged exposure and broader role familiarity. Employers increasingly value micro-credentials for their ability to demonstrate specific, up-to-date expertise and adaptability in fast-evolving fields such as technology and healthcare. These credentials offer a strategic advantage in competitive job markets by validating practical skills through concise, verifiable learning achievements.
Impact on Career Advancement: Tenure vs Micro-Credentials
Tenure experience often provides deep subject-matter expertise and long-term organizational loyalty, which can lead to stable career advancement within traditional or academic settings. Micro-credential experience focuses on acquiring specific, up-to-date skills that enhance adaptability and accelerate career mobility in fast-evolving industries. Combining tenure with micro-credentials offers a strategic advantage by blending foundational knowledge with current competencies, maximizing impact on career progression and marketability.
Hiring Trends: What Recruiters Prefer Today
Recruiters increasingly prioritize micro-credential experience over traditional tenure as it demonstrates up-to-date skills and adaptability in fast-evolving industries. Hiring trends show a shift towards valuing specific competencies validated by online certificates and short courses rather than years spent in a single role. Data indicates that candidates with targeted micro-credentials often outperform peers with longer tenure but outdated expertise.
Cost and Time Investment: Weighing Both Experiences
Tenure experience typically demands a higher time investment, often spanning several years to demonstrate consistent performance, while micro-credential experience focuses on acquiring specific, targeted skills in a shorter timeframe, usually weeks to months. Costs for tenure experience might include opportunity costs and slower income growth due to prolonged learning curves, whereas micro-credentials often require direct financial input for courses or certifications but can lead to faster skill validation and job market entry. Employers increasingly evaluate the balance between extensive tenure and specialized micro-credentials to optimize workforce efficiency and reduce training expenditures.
Adaptability and Skill Relevance in Dynamic Industries
Tenure experience offers deep industry knowledge and proven reliability, while micro-credential experience provides up-to-date, specialized skills that enhance adaptability in fast-changing industries. Employers prioritize micro-credentials for their alignment with emerging technologies and current market demands, ensuring skill relevance in dynamic environments. Combining traditional tenure with targeted micro-credentials strengthens workforce agility and long-term career growth.
Recognition and Credibility in the Job Market
Tenure experience offers long-term job stability and is widely recognized by employers, enhancing credibility through proven commitment and accumulated expertise. Micro-credential experience provides targeted, up-to-date skills that align with current industry demands, boosting recognition for specialized competencies in a rapidly evolving job market. Combining tenure with micro-credentials maximizes professional credibility and broadens recognition by showcasing both foundational knowledge and agile, continuous learning.
Case Studies: Successful Careers Built on Tenure vs Micro-Credentials
Case studies reveal that tenure experience provides deep institutional knowledge and long-term project involvement, crucial for leadership roles requiring strategic vision and organizational stability. Conversely, micro-credential experience demonstrates proficiency in niche skills and adaptability to emerging technologies, driving innovation in fast-evolving industries like IT and digital marketing. Employers increasingly value hybrid profiles combining tenure's depth with micro-credentials' agility, fostering career advancement through continuous upskilling and practical expertise.
Future Outlook: Balancing Tenure and Micro-credentials for Career Growth
Employers increasingly value a blend of tenure experience and micro-credentials, recognizing that long-term roles demonstrate reliability and deep industry knowledge while micro-credentials showcase adaptability and up-to-date skills in emerging technologies. Future career growth hinges on balancing these two, as tenure offers foundational expertise and micro-credentials provide targeted learning in specialized areas like AI, data analysis, and digital marketing. Integrating continuous learning through micro-credentials alongside sustained professional experience positions individuals for leadership roles and evolving job market demands.
Related Important Terms
Stackable Credentials Pathway
Tenure experience provides long-term professional development and institutional knowledge, while micro-credential experience offers targeted, skill-specific learning that can be stacked progressively to demonstrate expertise through the Stackable Credentials Pathway. Combining both enhances career advancement by validating comprehensive tenure achievements alongside agile, verifiable micro-credential competencies.
Micro-Accumulation Tenure
Micro-Accumulation Tenure emphasizes the progressive acquisition of skills through multiple micro-credentials, offering a flexible and targeted alternative to traditional tenure experience. This approach enables professionals to demonstrate competency and adaptability in specific areas, enhancing career development with validated, bite-sized learning achievements.
Skill-Badging Versus Laddering
Tenure experience reflects long-term commitment and role progression within an organization, emphasizing laddering that aligns with hierarchical advancement, while micro-credential experience prioritizes skill-badging, showcasing specific competencies through short, targeted certifications valued in dynamic job markets. Skill-badging offers granular validation of expertise that complements traditional tenure by enabling professionals to demonstrate up-to-date, job-relevant skills, enhancing adaptability and employability.
Modular Experience Portfolio
Tenure experience reflects long-term, in-depth expertise in a specific role or organization, while micro-credential experience highlights targeted, verified skills acquired through modular learning units. A Modular Experience Portfolio integrates both, showcasing comprehensive capabilities through accumulated credentials and sustained professional contributions.
Nano-Degree Career Tracks
Tenure experience often reflects long-term commitment and depth in a specific field, whereas micro-credential experience, particularly with Nano-Degree Career Tracks, emphasizes specialized skills and rapid competency development tailored to emerging industry demands. Employers increasingly value Nano-Degree Career Tracks for their ability to validate up-to-date expertise and adaptability in fast-evolving job roles.
Agile Tenure Mapping
Agile Tenure Mapping prioritizes micro-credential experience by quantifying specific skills and project outcomes over traditional tenure length, enabling more accurate assessment of candidates' agility and adaptability in dynamic environments. This approach emphasizes verified competencies attained through targeted micro-credentials, reflecting current expertise and practical application rather than mere duration of service.
Short-Cycle Competency Recognition
Short-cycle competency recognition through micro-credential experience offers targeted skill verification that complements traditional tenure by validating specific, up-to-date proficiencies relevant to evolving job requirements. This approach enhances workforce adaptability and provides employers with precise indicators of current capabilities beyond the duration of service alone.
Immersive Upskilling Timeline
Tenure experience offers cumulative knowledge gained over extended periods, while micro-credential experience emphasizes targeted skills acquired through immersive upskilling timelines, accelerating competency in specialized areas. Organizations increasingly value micro-credentials for their ability to rapidly close skill gaps, complementing traditional tenure with precise, verifiable expertise.
Disruptive Experience Validation
Tenure experience often reflects prolonged exposure and stability within a field, while micro-credential experience emphasizes specialized, up-to-date skills validated through digital badges or certificates, enabling rapid adaptation to emerging industry trends. Disruptive experience validation leverages micro-credentials to more accurately measure relevant competencies and innovation capacity, challenging traditional tenure metrics in talent assessment.
Tenureless Talent Advancement
Tenureless talent advancement prioritizes micro-credential experience by validating specific skills and competencies acquired through short-term, targeted learning over traditional time-based tenure metrics. This approach accelerates career progression by emphasizing demonstrated expertise and practical achievements rather than years spent in a position.
Tenure experience vs Micro-credential experience for positions Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com