Professional background provides specialized knowledge and industry-specific expertise that directly supports job performance, while transferable skills such as communication, problem-solving, and adaptability enhance versatility across roles and sectors. Experience gained from diverse job functions strengthens these transferable skills, making candidates more resilient and capable in dynamic work environments. Balancing both professional background and transferable skills enables pet owners and animal care professionals to deliver comprehensive, high-quality experiences.
Table of Comparison
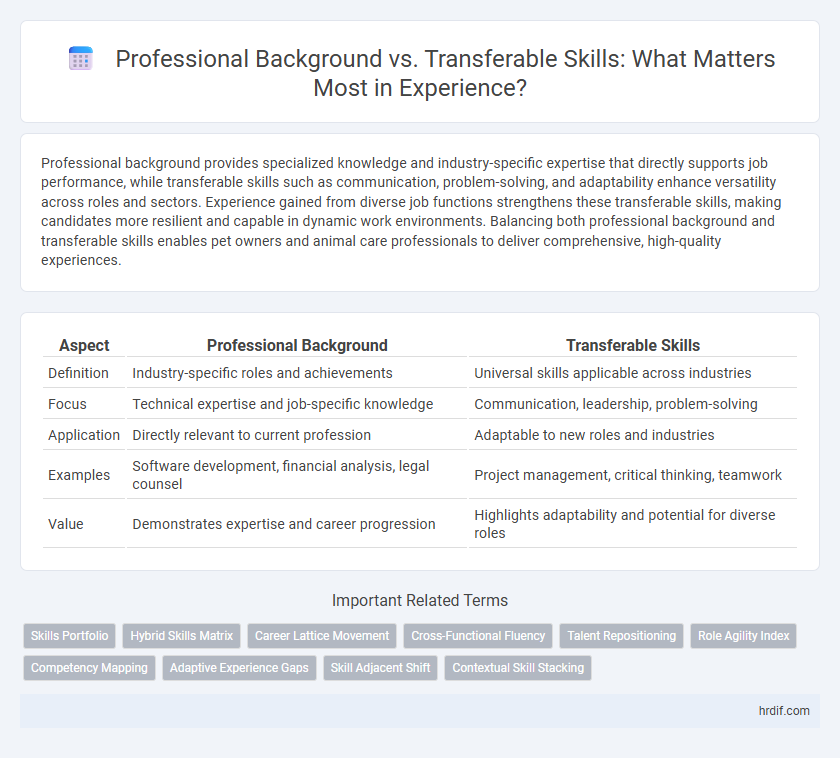
| Aspect | Professional Background | Transferable Skills |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Industry-specific roles and achievements | Universal skills applicable across industries |
| Focus | Technical expertise and job-specific knowledge | Communication, leadership, problem-solving |
| Application | Directly relevant to current profession | Adaptable to new roles and industries |
| Examples | Software development, financial analysis, legal counsel | Project management, critical thinking, teamwork |
| Value | Demonstrates expertise and career progression | Highlights adaptability and potential for diverse roles |
Defining Professional Background
Professional background encompasses the specific roles, industries, and accomplishments that define an individual's career trajectory and expertise. It highlights formal employment history, education, certifications, and specialized knowledge gained within a particular field. Defining professional background provides a concrete foundation to assess qualifications, whereas transferable skills emphasize adaptable abilities applicable across various roles and sectors.
Understanding Transferable Skills
Professional background provides specific industry expertise and technical knowledge from previous roles, while transferable skills encompass adaptable abilities such as communication, problem-solving, and leadership that apply across diverse job functions. Understanding transferable skills is crucial for career mobility, enabling individuals to leverage experiences from various fields to succeed in new environments. Employers increasingly value these versatile competencies as indicators of potential and adaptability in dynamic workplaces.
Key Differences between Professional Background and Transferable Skills
Professional background refers to specific roles, industries, and technical expertise accumulated through formal employment, highlighting job titles, companies, and projects directly related to a field. Transferable skills encompass versatile abilities such as communication, problem-solving, and leadership that can be applied across various jobs and industries regardless of professional history. The key difference lies in professional background emphasizing specialized experience, while transferable skills focus on adaptable talents that enhance employability in diverse roles.
Importance of Professional Background in Career Development
A strong professional background provides specialized expertise and credibility that can accelerate career growth and open doors to advanced opportunities in a specific industry. While transferable skills such as communication and problem-solving enhance adaptability, professional background anchors an individual's value through demonstrated accomplishments and industry-specific knowledge. Employers prioritize candidates with relevant professional histories because they deliver immediate impact and long-term strategic benefits.
The Role of Transferable Skills in Career Transitions
Transferable skills such as communication, problem-solving, and leadership play a crucial role in career transitions by enabling professionals to adapt to new industries and roles efficiently. While professional background provides specific industry knowledge, transferable skills offer versatility that employers value across various sectors. Leveraging these skills can accelerate career growth and open opportunities beyond one's original field.
Showcasing Professional Background on Your Resume
Showcasing your professional background on your resume highlights specific roles, industries, and accomplishments that demonstrate your expertise and reliability in a particular field. Emphasizing measurable achievements and relevant job titles attracts employers seeking proven experience and domain knowledge. Incorporating keywords from job descriptions optimizes your resume for applicant tracking systems, increasing visibility to hiring managers.
Highlighting Transferable Skills during the Job Search
Transferable skills, such as communication, problem-solving, and leadership, offer valuable advantages across various industries and roles, enhancing employability beyond specific professional backgrounds. Emphasizing these adaptable skills during the job search helps candidates demonstrate versatility and potential for success in diverse work environments. Employers increasingly prioritize candidates who showcase transferable skills that align with organizational needs and culture.
Bridging Gaps: Combining Background with Transferable Skills
Combining professional background with transferable skills bridges gaps in experience by enhancing adaptability and broadening career opportunities. Transferable skills such as communication, problem-solving, and project management complement specialized knowledge, enabling seamless transitions across industries. Employers value candidates who leverage both domain expertise and versatile abilities to drive innovation and efficiency.
Assessing the Value of Your Experience: Background vs. Transferable Skills
Evaluating your professional background alongside transferable skills reveals the full scope of your experience's value in career advancement. Industry-specific expertise demonstrates deep knowledge while transferable skills like communication, problem-solving, and adaptability enhance versatility across roles. Balancing both aspects enables effective positioning in diverse job markets and maximizes employability.
Strategies to Develop Both Professional Background and Transferable Skills
Building a robust professional background involves targeted industry experience, certifications, and specialized training that demonstrate expertise and commitment. Developing transferable skills such as communication, problem-solving, and adaptability requires engaging in diverse roles, continuous learning, and active networking to enhance versatility across various fields. Combining strategic job rotations, mentorship programs, and skill-based workshops accelerates growth in both professional qualifications and universally applicable competencies.
Related Important Terms
Skills Portfolio
A Skills Portfolio highlights transferable skills such as communication, problem-solving, and leadership that complement a professional background rooted in industry-specific experience, enhancing employability across diverse roles. Emphasizing both technical expertise and soft skills creates a comprehensive experience profile that adapts to evolving career opportunities.
Hybrid Skills Matrix
Hybrid Skills Matrix integrates professional background with transferable skills, enabling a comprehensive assessment of expertise across diverse roles and industries. This approach highlights the synergy between domain-specific knowledge and adaptable competencies, optimizing workforce versatility and career development.
Career Lattice Movement
Professional background provides industry-specific expertise essential for vertical career advancements, while transferable skills such as communication, problem-solving, and adaptability enable lateral and diagonal moves within a career lattice. Emphasizing transferable skills facilitates career lattice movement by allowing professionals to navigate diverse roles and functions beyond their original specialization.
Cross-Functional Fluency
Professional background provides specialized expertise within a specific industry, while transferable skills enable cross-functional fluency by facilitating effective communication and collaboration across diverse departments. Mastering transferable skills such as problem-solving, adaptability, and interpersonal communication enhances an individual's ability to navigate and integrate knowledge from multiple disciplines.
Talent Repositioning
Talent repositioning hinges on leveraging transferable skills such as leadership, communication, and problem-solving rather than solely relying on a professional background in a specific industry. Employers increasingly value adaptable competencies that enable candidates to thrive across diverse roles, fostering career growth and seamless transitions.
Role Agility Index
The Role Agility Index highlights the importance of transferable skills over professional background by measuring an individual's adaptability across various roles and industries. This index quantifies competencies like problem-solving, communication, and leadership, demonstrating how flexible skillsets drive career mobility despite differing job histories.
Competency Mapping
Professional background provides industry-specific expertise critical for precise role alignment, while transferable skills enable adaptability across diverse functions, enhancing overall competency mapping effectiveness. Emphasizing both elements in competency mapping ensures a comprehensive evaluation of capabilities, facilitating optimal talent utilization and career development strategies.
Adaptive Experience Gaps
Adaptive experience gaps arise when professional backgrounds lack direct industry-specific expertise, yet transferable skills like problem-solving, communication, and project management enable candidates to bridge these gaps effectively. Employers increasingly value adaptive candidates who demonstrate continuous learning and the ability to apply versatile skills across varying roles, facilitating smoother transitions and innovation.
Skill Adjacent Shift
Skill adjacent shifts enhance professional background by applying transferable skills to new industries, enabling seamless career transitions. Emphasizing adaptability and related competencies accelerates growth beyond traditional role limitations.
Contextual Skill Stacking
Professional background shapes specialized expertise within a defined industry, while transferable skills enable adaptability across diverse roles by leveraging contextual skill stacking to blend technical knowledge with soft skills. This strategic combination amplifies career flexibility and enhances problem-solving capacity in dynamic work environments.
Professional background vs Transferable skills for experience. Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com