Experience provides in-depth knowledge and long-term skill development, making it highly valuable for building a strong professional portfolio. Micro-internships offer short-term, project-based opportunities that allow quick exposure to various tasks but may lack the depth and continuity of traditional experience. Employers often prioritize sustained work experience over brief engagements when evaluating candidate credentials.
Table of Comparison
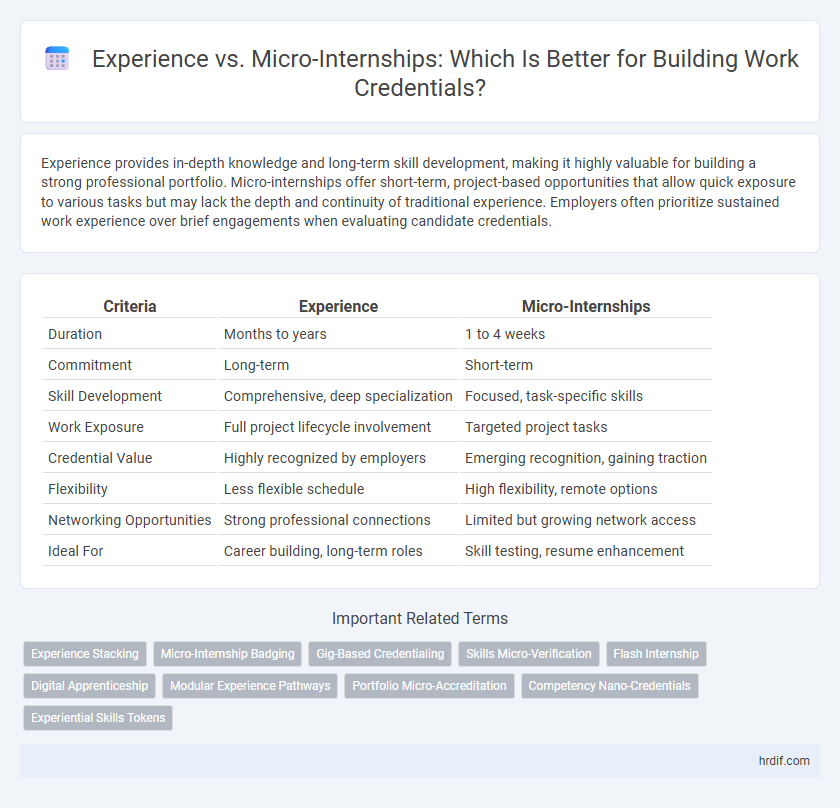
| Criteria | Experience | Micro-Internships |
|---|---|---|
| Duration | Months to years | 1 to 4 weeks |
| Commitment | Long-term | Short-term |
| Skill Development | Comprehensive, deep specialization | Focused, task-specific skills |
| Work Exposure | Full project lifecycle involvement | Targeted project tasks |
| Credential Value | Highly recognized by employers | Emerging recognition, gaining traction |
| Flexibility | Less flexible schedule | High flexibility, remote options |
| Networking Opportunities | Strong professional connections | Limited but growing network access |
| Ideal For | Career building, long-term roles | Skill testing, resume enhancement |
Defining Traditional Experience vs Micro-Internships
Traditional experience typically involves long-term employment or internships that provide in-depth exposure to industry practices, project management, and organizational culture over months or years. Micro-internships are short-term, project-based assignments lasting a few weeks, designed to deliver specific skills and real-world tasks that employers can evaluate quickly. Both forms of work credentials offer valuable practical knowledge, but traditional experience often emphasizes sustained responsibility, while micro-internships highlight agility and targeted skill application.
The Evolution of Work Credentials
The evolution of work credentials highlights a growing preference for micro-internships as flexible alternatives to traditional experience, offering targeted skill validation in shorter timeframes. Employers increasingly value micro-internships for providing real-world project outcomes that align closely with industry needs, accelerating talent acquisition and reducing the ambiguity of generalized work experience. This shift underscores a transformative approach in credentialing, where demonstrable competencies from micro-internships are prioritized over the duration-based metrics of conventional experience.
Skills Gained: Long-term Roles vs Short-term Projects
Long-term roles provide deep skill development through sustained responsibilities, enabling mastery in specific areas and fostering strategic thinking. Micro-internships offer diverse, project-based experiences that enhance adaptability and problem-solving skills in a condensed timeframe. Both contribute valuable credentials, with long-term roles emphasizing depth and micro-internships emphasizing breadth of skills.
Accessibility and Inclusivity in Micro-Internships
Micro-internships offer enhanced accessibility and inclusivity by providing flexible, short-term project opportunities that accommodate diverse schedules and backgrounds, breaking down traditional barriers to gaining professional experience. These platforms often utilize virtual formats, enabling participation from underrepresented groups and individuals in remote or underserved areas. Consequently, micro-internships democratize work credentials by expanding access beyond conventional internships, fostering a more equitable workforce development.
Resume Impact: How Employers View Each
Employers often regard traditional work experience as a stronger indicator of long-term commitment and skill development, enhancing a resume with proven responsibilities and achievements. Micro-internships provide valuable, project-based exposure that highlights adaptability and specific competencies but may be perceived as less comprehensive than sustained roles. Resumes combining both can demonstrate versatility while showcasing depth and breadth in practical experience.
Networking Opportunities Compared
Experience offers deeper networking opportunities by fostering sustained professional relationships and industry connections through long-term projects and consistent team collaboration. Micro-internships provide brief, task-oriented engagements that allow for quick exposure to diverse companies but limit the depth and quality of networking compared to extended experiences. Professionals seeking to build meaningful contacts and mentorship opportunities benefit more from traditional experience over micro-internships.
Depth vs Breadth of Learning
Experience offers depth in skill development through sustained, real-world projects that build expertise and professional judgment over time. Micro-internships provide breadth by exposing individuals to diverse tasks and industries in short bursts, enhancing adaptability and varied knowledge. Prioritizing depth-focused experience cultivates mastery, while breadth-oriented micro-internships foster versatility in work credentials.
Time Commitment and Flexibility
Experience offers long-term skill development and deeper industry insights but typically demands a significant, fixed time commitment. Micro-internships provide flexible, short-term projects that allow individuals to gain credentials without disrupting existing schedules. These brief engagements suit professionals seeking to balance work, learning, and personal commitments efficiently.
Industry Trends and Future of Credentials
Industry trends emphasize the growing importance of micro-internships as flexible, skill-focused credentials complementing traditional work experience. Employers increasingly value micro-internships for providing verifiable, project-based achievements that align with rapidly evolving job requirements. The future of credentials is likely to blend comprehensive experience with targeted micro-internship portfolios, enhancing talent evaluation and workforce readiness.
Choosing the Right Path for Career Growth
Choosing between traditional work experience and micro-internships depends on your career goals and industry demands. Traditional experience often provides in-depth skill development and long-term projects, enhancing your resume with substantial responsibilities. Micro-internships offer flexible, short-term tasks that build specific skills quickly and expand your professional network, making them ideal for gaining diverse exposure and accelerating career growth.
Related Important Terms
Experience Stacking
Experience stacking enhances professional credentials more effectively than isolated micro-internships by accumulating diverse, real-world skills across multiple roles. This layered approach creates a comprehensive portfolio that demonstrates sustained growth and adaptability, crucial for competitive job markets.
Micro-Internship Badging
Micro-Internship badging offers a verifiable digital credential that highlights specific skills and project experience, providing employers with clear evidence of competencies beyond traditional work experience. This form of credentialing enhances candidate profiles by showcasing targeted achievements and practical contributions within short-term assignments, making it a valuable supplement to conventional resumes.
Gig-Based Credentialing
Gig-based credentialing offers practical, project-specific proof of skills that often hold more immediate relevance for employers than traditional micro-internships, which can be limited in scope and duration. Experience gained through gig platforms demonstrates adaptability and real-world problem-solving, providing a dynamic portfolio that enhances work credentials effectively.
Skills Micro-Verification
Skills micro-verification in micro-internships offers targeted validation of specific competencies, enhancing work credentials more efficiently than traditional experience by providing real-time, skill-based proof in niche areas. This approach accelerates employability through focused assessment and demonstrable expertise, contrasting with broader, often less quantifiable traditional experience.
Flash Internship
Flash Internships offer concise, project-based work experience that delivers relevant skills and tangible results faster than traditional micro-internships, making them ideal for building credible work credentials. Emphasizing focused, hands-on tasks, Flash Internships enhance portfolio value and demonstrate practical expertise to employers more efficiently.
Digital Apprenticeship
Digital Apprenticeships offer immersive, hands-on experience that often exceeds the scope of traditional micro-internships by providing structured skill development and real-world project involvement. These programs enhance work credentials by blending theoretical knowledge with practical application, resulting in a more comprehensive professional profile.
Modular Experience Pathways
Modular Experience Pathways offer a flexible alternative to traditional work credentials by breaking down professional skills into focused, stackable micro-internships that build verified competencies. This approach enhances employability by providing targeted, real-world experience that aligns with industry needs more precisely than generalized experience alone.
Portfolio Micro-Accreditation
Portfolio Micro-Accreditation through micro-internships offers targeted, verifiable credentials that showcase specific skills and project outcomes, enhancing employability beyond traditional broad work experience. This approach enables professionals to build a diverse portfolio of validated competencies, aligning with employer demand for measurable expertise and faster career progression.
Competency Nano-Credentials
Competency nano-credentials gained through micro-internships provide targeted skill validation that enhances traditional work experience by offering verifiable proof of specific capabilities. These bite-sized credentials enable employers to assess practical competencies efficiently, complementing broader experiential learning with focused, industry-relevant qualifications.
Experiential Skills Tokens
Experiential Skills Tokens provide verifiable proof of practical skills gained through hands-on work experiences, offering more nuanced validation than micro-internships, which often focus on short-term task completion. These tokens enhance professional credibility by documenting specific competencies developed, making them a more robust tool for showcasing experiential learning in work credentials.
Experience vs Micro-Internships for work credentials. Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com