Experience pet refers to hands-on, practical experience gained directly in the pet care industry, showcasing an individual's ability to manage real-life animal care situations. Gig experience, typical of short-term or freelance roles, may demonstrate versatility and adaptability but often lacks the depth and consistency required for full-time employment eligibility. Employers prioritize Experience pet as it indicates sustained responsibility and proficiency essential for reliable pet care jobs.
Table of Comparison
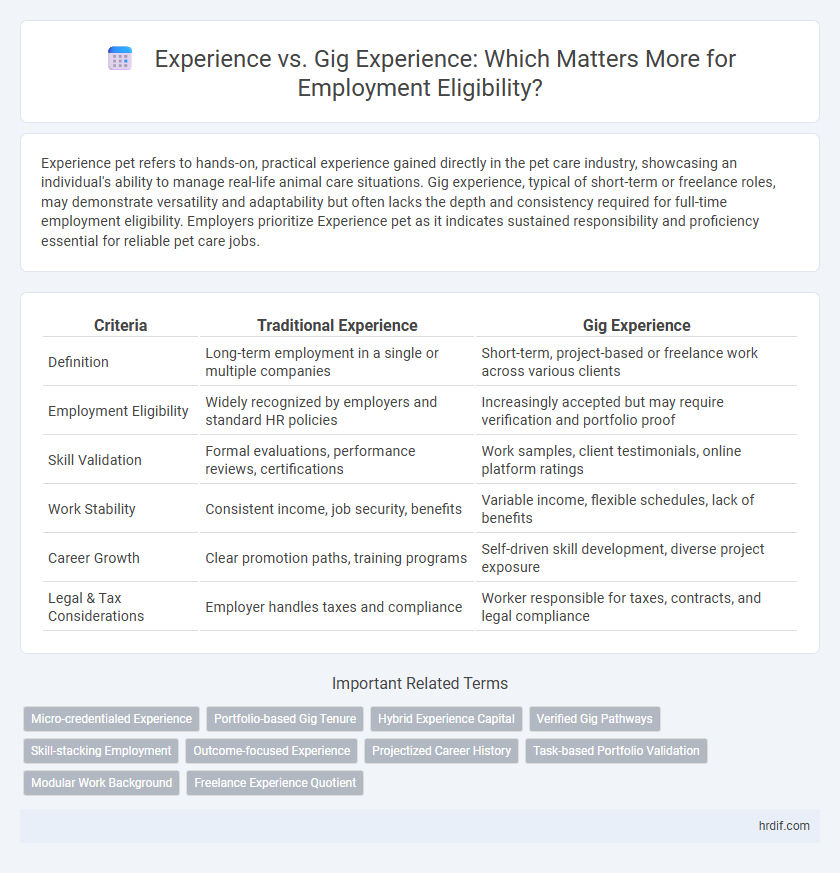
| Criteria | Traditional Experience | Gig Experience |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Long-term employment in a single or multiple companies | Short-term, project-based or freelance work across various clients |
| Employment Eligibility | Widely recognized by employers and standard HR policies | Increasingly accepted but may require verification and portfolio proof |
| Skill Validation | Formal evaluations, performance reviews, certifications | Work samples, client testimonials, online platform ratings |
| Work Stability | Consistent income, job security, benefits | Variable income, flexible schedules, lack of benefits |
| Career Growth | Clear promotion paths, training programs | Self-driven skill development, diverse project exposure |
| Legal & Tax Considerations | Employer handles taxes and compliance | Worker responsible for taxes, contracts, and legal compliance |
Defining Traditional Experience vs Gig Experience
Traditional experience refers to continuous, long-term employment within established companies, emphasizing stable job roles, structured responsibilities, and steady career progression. Gig experience involves short-term, project-based work or freelance tasks, often through digital platforms, highlighting flexibility, diverse skill application, and independent contract management. Employers increasingly assess both types to gauge adaptability, skill diversity, and real-world problem-solving capabilities in potential candidates.
The Evolution of Work: From Careers to Gigs
The evolution of work has shifted from traditional long-term careers to flexible gig experiences, changing how employers evaluate eligibility. Gig experience emphasizes project-based skills and adaptability, often showcasing diverse competencies across multiple roles rather than tenure at a single employer. Employment eligibility now increasingly values measurable outcomes and relevant expertise gained through gig work, reflecting modern workforce dynamics.
Key Differences Between Experience Types
Experience refers to sustained employment within a particular role or industry, often highlighting deep expertise and long-term skill development, whereas gig experience involves short-term, project-based tasks typically found in freelance or contract work. Employment eligibility can be impacted by these distinctions, as traditional employers may prioritize continuous experience for roles requiring stability and proven commitment, while gig experience showcases adaptability and a diverse skill set valued in dynamic or project-driven environments. Understanding the key differences between experience types helps job seekers tailor their resumes and applications to better match employer expectations and industry requirements.
Evaluating Skills: Gig Work vs Traditional Roles
Evaluating skills in gig work versus traditional roles reveals distinct approaches to employment eligibility, where gig experience often highlights adaptability, self-management, and project-based accomplishments. Traditional roles emphasize consistent performance, long-term responsibility, and hierarchical skill development within established organizational structures. Employers assessing eligibility weigh the depth of skills gained through gig work's diverse tasks against the structured expertise cultivated in conventional employment.
Employer Perceptions of Gig Experience
Employer perceptions of gig experience often vary depending on the industry and the relevance of skills demonstrated during gigs. Many employers value gig experience that showcases adaptability, self-management, and specific technical abilities, recognizing its contribution to a candidate's overall expertise. However, some hiring managers may question the depth and stability of gig roles compared to traditional employment, impacting eligibility evaluations.
Transferable Skills from Gig Work
Transferable skills gained from gig work, such as project management, communication, and problem-solving, significantly enhance employment eligibility by demonstrating adaptability and self-motivation. Unlike traditional experience, gig experience reflects a diverse portfolio of real-world tasks that showcase an individual's ability to work independently and manage multiple responsibilities. Employers increasingly recognize gig experience as a valid indicator of competence and readiness for various professional roles.
The Impact on Employability and Job Eligibility
Experience directly correlates with job eligibility by demonstrating a candidate's ability to perform specific roles, while gig experience reflects flexibility and diverse skill application across multiple short-term tasks. Employers increasingly value gig experience for its evidence of adaptability and problem-solving in dynamic environments, broadening eligibility criteria beyond traditional long-term positions. The impact on employability lies in balancing both sustained expertise and varied project involvement to meet evolving job market demands.
Bridging the Gap: Combining Both Experiences
Combining traditional work experience with gig experience creates a comprehensive profile that enhances employment eligibility by showcasing adaptability and diverse skill sets. Employers value candidates who demonstrate the ability to navigate both structured environments and flexible, project-based roles, reflecting a broader range of competencies. Bridging this gap ensures candidates leverage both forms of experience to meet dynamic job market demands effectively.
Challenges Faced by Gig Workers in Employment
Gig workers often encounter challenges such as inconsistent income, lack of job security, and limited access to traditional employment benefits, which can complicate the validation of their experience for formal job applications. Employers may question the reliability and relevance of gig experience due to its project-based nature and absence of standardized roles, impacting eligibility assessments. Navigating these concerns requires clear documentation of skills acquired and demonstrable outcomes to align gig experience with conventional employment criteria.
Future Trends: The Changing Value of Experience
Future trends in employment emphasize the growing importance of gig experience alongside traditional experience, reflecting shifts in workforce dynamics. Employers increasingly value diverse project-based skills and adaptability gained through gig roles, recognizing them as indicators of flexibility and innovation. This evolving perspective reshapes eligibility criteria, blending conventional career paths with the gig economy's experiential relevance.
Related Important Terms
Micro-credentialed Experience
Micro-credentialed experience offers targeted validation of specific skills and competencies, making it increasingly recognized by employers as a reliable indicator of job readiness compared to traditional gig experience. This form of verified experience bridges the gap between informal gig work and formal employment by providing documented proof of expertise aligned with industry standards.
Portfolio-based Gig Tenure
Portfolio-based gig tenure showcases a candidate's sustained performance and verified outcomes across multiple projects, often providing a more comprehensive measure of skills than traditional employment experience. Employers increasingly recognize this gig experience as valid for eligibility, especially when supported by detailed portfolios that demonstrate consistent value delivery over time.
Hybrid Experience Capital
Hybrid Experience Capital integrates traditional professional experience with gig economy roles, providing a comprehensive evaluation metric for employment eligibility. Employers increasingly value this blended experience model, recognizing its ability to demonstrate adaptability, diverse skill sets, and modern work dynamics.
Verified Gig Pathways
Verified Gig Pathways offer authenticated project-based work experiences that enhance employment eligibility by providing concrete, skill-specific proofs recognized by industry employers. Unlike traditional experience, these verified gigs demonstrate real-time, verifiable competencies through digital credentials, bridging the gap between gig economy roles and formal job qualifications.
Skill-stacking Employment
Skill-stacking employment leverages a combination of diverse gig experiences and formal work history to enhance eligibility by demonstrating versatile, adaptable capabilities across multiple industries. Employers increasingly value gig experience for its real-world problem-solving skills and practical knowledge, which complement traditional experience to create a comprehensive skill set.
Outcome-focused Experience
Outcome-focused experience emphasizes tangible achievements and measurable results gained through consistent project involvement, distinguishing it from gig experience that often comprises short-term, task-based roles. Employers prioritize outcome-focused experience for employment eligibility because it demonstrates proven skills, problem-solving capabilities, and the ability to contribute to long-term organizational goals.
Projectized Career History
Projectized career history emphasizes long-term, end-to-end project leadership over short-term gig experiences, demonstrating deeper expertise and consistent performance in complex roles. Employers often prioritize projectized experience as it reflects comprehensive skills in planning, execution, and delivery, essential for sustained business impact.
Task-based Portfolio Validation
Task-based portfolio validation offers a more precise measure of relevant skills compared to traditional gig experience by showcasing applicants' ability to complete specific projects aligned with job requirements. Employers prioritize this evidence of demonstrated competency, which directly correlates with employment eligibility and reduces reliance on duration-based experience claims.
Modular Work Background
Modular work background highlights specific skill sets and project-based accomplishments, offering a more targeted representation of expertise compared to traditional gig experience, which often emphasizes quantity over quality. Employers prioritize modular work experience for its clarity in demonstrating relevant competencies and adaptability in dynamic job roles.
Freelance Experience Quotient
Freelance Experience Quotient (FEQ) quantifies project diversity, client feedback, and problem-solving skills, distinguishing it from traditional gig experience which often emphasizes task completion over strategic impact. Employers increasingly prioritize high FEQ freelancers for roles requiring adaptability and innovation, recognizing this metric as a reliable indicator of comprehensive professional capability.
Experience vs Gig Experience for employment eligibility. Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com