Employers prioritize strategic oversight and resource allocation to ensure organizational goals are met, while distributed team leaders emphasize real-time coordination and communication across diverse, remote team members. Employers set broad policies and long-term objectives, whereas distributed team leaders focus on managing day-to-day workflows and overcoming challenges of geographical dispersion. Effective management requires balancing the employer's vision with the distributed leader's ability to maintain team cohesion and productivity.
Table of Comparison
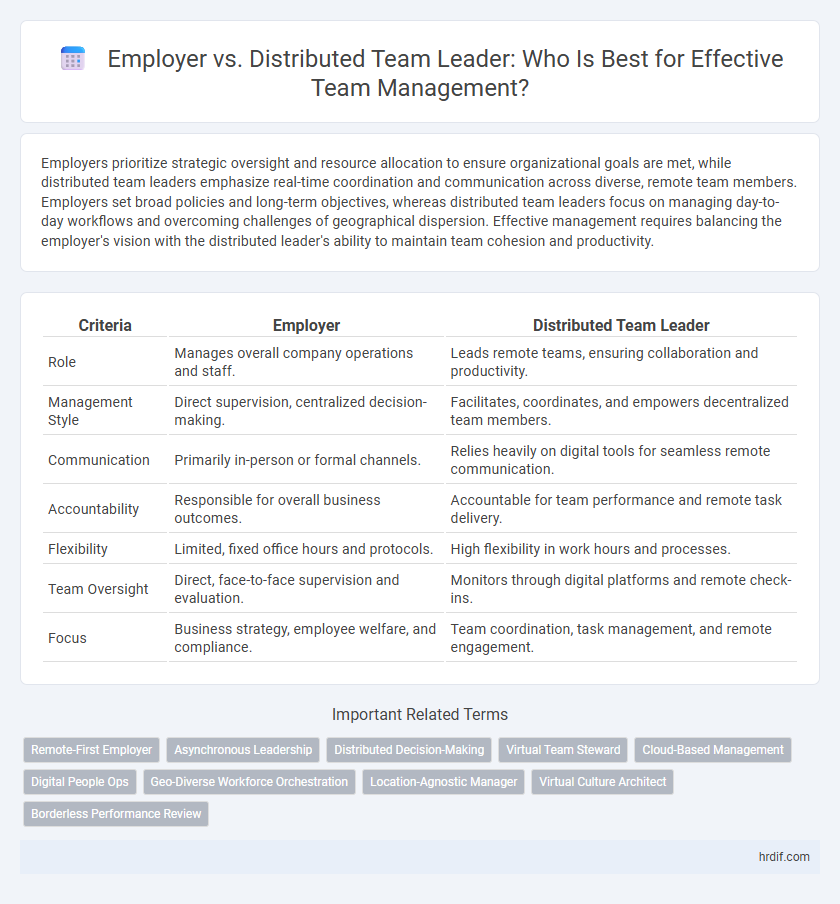
| Criteria | Employer | Distributed Team Leader |
|---|---|---|
| Role | Manages overall company operations and staff. | Leads remote teams, ensuring collaboration and productivity. |
| Management Style | Direct supervision, centralized decision-making. | Facilitates, coordinates, and empowers decentralized team members. |
| Communication | Primarily in-person or formal channels. | Relies heavily on digital tools for seamless remote communication. |
| Accountability | Responsible for overall business outcomes. | Accountable for team performance and remote task delivery. |
| Flexibility | Limited, fixed office hours and protocols. | High flexibility in work hours and processes. |
| Team Oversight | Direct, face-to-face supervision and evaluation. | Monitors through digital platforms and remote check-ins. |
| Focus | Business strategy, employee welfare, and compliance. | Team coordination, task management, and remote engagement. |
Defining the Employer and Distributed Team Leader Roles
The employer holds the ultimate authority in setting organizational goals, defining job roles, and allocating resources while ensuring legal compliance and employee welfare. In contrast, the distributed team leader focuses on coordinating remote team members, maintaining communication across different time zones, and fostering collaboration without direct supervision. Clear role delineation between employer and distributed team leader optimizes productivity and supports effective remote workforce management.
Core Responsibilities: Employer vs. Distributed Team Leader
Employers primarily focus on defining organizational goals, ensuring compliance with labor laws, and managing resource allocation to achieve business objectives. Distributed Team Leaders emphasize coordinating remote team activities, fostering communication across time zones, and monitoring productivity through digital collaboration tools. Both roles require strategic decision-making, but Employers prioritize overall organizational success while Distributed Team Leaders specialize in operational efficiency within virtual environments.
Decision-Making Processes in Both Management Styles
Employers typically centralize decision-making processes, maintaining direct control and swift execution within established hierarchies. Distributed Team Leaders foster collaborative decision-making across diverse locations, leveraging digital tools to ensure inclusivity and real-time coordination. Both management styles impact agility and accountability, with Employers favoring structured authority and Distributed Team Leaders emphasizing decentralized empowerment.
Communication Strategies and Challenges
Employers and distributed team leaders face unique communication challenges that impact team collaboration and productivity, such as time zone differences, cultural barriers, and technology reliance. Effective communication strategies include implementing regular virtual meetings, using collaborative platforms like Slack or Microsoft Teams, and establishing clear expectations for responsiveness and reporting. Employers must balance oversight with autonomy, ensuring distributed leaders foster trust while maintaining alignment with organizational goals.
Leadership Approach: Centralized vs. Distributed Teams
Employers often favor a centralized leadership approach, maintaining direct control over decision-making to ensure consistency and alignment with organizational goals. Distributed team leaders adopt a decentralized management style, empowering remote members with autonomy and fostering collaboration across diverse locations. This contrast impacts communication flow, accountability structures, and agility in response to changing project requirements.
Accountability and Performance Management
Employers prioritize clear accountability frameworks to ensure consistent performance management across all roles, emphasizing direct supervision and standardized evaluation metrics. In contrast, distributed team leaders leverage flexible accountability methods tailored to remote or hybrid settings, focusing on outcome-based performance and asynchronous communication tools. Both roles require robust performance tracking systems, but employers maintain centralized control while distributed team leaders adapt management styles to foster autonomy and trust.
Employee Engagement and Motivation Tactics
Employers prioritize structured oversight and clear hierarchy to ensure accountability and performance consistency, while distributed team leaders emphasize autonomy and flexible communication to boost employee engagement. Effective motivation tactics in distributed teams include personalized recognition, trust-building practices, and leveraging digital collaboration tools that foster inclusivity. Both roles require adaptive strategies tailored to their organizational models to maintain high productivity and employee satisfaction.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Each Role
Employers hold centralized authority, enabling streamlined decision-making and consistent policy enforcement but may suffer from limited flexibility and slower adaptation in dynamic markets. Distributed Team Leaders excel in managing geographically dispersed teams, fostering autonomy and real-time responsiveness, yet face challenges in maintaining communication consistency and ensuring alignment with organizational goals. Balancing control with flexibility, Employers maintain overall strategic direction whereas Distributed Team Leaders enhance operational agility across diverse locations.
Impact on Team Productivity and Collaboration
Employers who take a hands-on approach often experience more direct control over workflows, which can lead to clearer expectations and faster decision-making. Distributed team leaders emphasize asynchronous communication tools and flexible schedules, fostering autonomy and innovation within diverse teams. This balance impacts team productivity by blending structured oversight with adaptive collaboration, optimizing overall performance.
Choosing the Right Role for Your Organization
Selecting between an employer and a distributed team leader hinges on your organization's structure and goals. Employers oversee traditional management responsibilities such as hiring, payroll, and compliance, while distributed team leaders focus on coordinating remote teams, fostering communication, and ensuring productivity across locations. Evaluating your operational needs and team dynamics helps determine the most effective leadership role to drive organizational success.
Related Important Terms
Remote-First Employer
A Remote-First Employer prioritizes asynchronous communication and trust-based accountability, enhancing productivity by leveraging diverse, geographically dispersed talent. In contrast, a Distributed Team Leader focuses on coordinating day-to-day operations and maintaining real-time collaboration, often using digital tools to bridge the gap between remote and in-office team members.
Asynchronous Leadership
Employers benefit from adopting asynchronous leadership in managing distributed teams by empowering productivity across different time zones without requiring real-time supervision. Emphasizing clear communication, goal-setting, and trust supports autonomy and accountability, which enhances team efficiency and engagement in global operations.
Distributed Decision-Making
Employers benefit from distributed team leaders who enable decentralized decision-making, fostering agility and responsiveness across remote or hybrid teams. This approach enhances productivity by empowering team members with autonomy while maintaining strategic alignment through clear communication channels.
Virtual Team Steward
Virtual Team Stewards enhance employer management by facilitating seamless communication and accountability across distributed teams, leveraging digital tools to track productivity and employee engagement efficiently. Their role bridges geographic and cultural gaps, ensuring employers maintain consistent oversight and foster collaboration within remote or hybrid work environments.
Cloud-Based Management
Employer-driven management leverages centralized control and standardized protocols to ensure compliance and consistent performance across departments. Distributed team leaders utilize cloud-based management platforms to enable real-time collaboration, decentralized decision-making, and scalable project tracking, enhancing agility and responsiveness in remote work environments.
Digital People Ops
Employers leveraging Digital People Ops benefit from centralized control and streamlined compliance, while Distributed Team Leaders excel in fostering autonomy and real-time collaboration across remote locations. Digital People Ops integrates HR technology to optimize workforce management, enhancing productivity and employee engagement within both traditional and distributed team structures.
Geo-Diverse Workforce Orchestration
Employers managing geo-diverse workforces benefit from distributed team leaders who specialize in coordinating cross-cultural communication and leveraging regional expertise to enhance productivity. These leaders utilize digital collaboration tools and localized management strategies to synchronize team efforts across multiple time zones, driving seamless project delivery and organizational cohesion.
Location-Agnostic Manager
A Location-Agnostic Manager enhances productivity by leveraging remote talent across multiple time zones, reducing overhead costs compared to traditional Employers. Distributed Team Leaders excel in fostering collaboration through digital tools, enabling seamless communication and efficient performance tracking regardless of physical location.
Virtual Culture Architect
An Employer fosters organizational growth by aligning company goals with employee performance, while a Distributed Team Leader excels in managing remote teams through flexible communication and trust-building strategies. The Virtual Culture Architect plays a crucial role by designing and sustaining an inclusive digital work environment that enhances collaboration, engagement, and productivity across geographically dispersed teams.
Borderless Performance Review
Employers transitioning from traditional management to distributed team leadership benefit from Borderless Performance Review systems that enable real-time, location-independent feedback and evaluation. This approach enhances transparency, accountability, and productivity across global teams by leveraging digital tools optimized for seamless performance monitoring and collaborative goal setting.
Employer vs Distributed Team Leader for management. Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com