Traditional workers often thrive in structured environments with clear roles, consistent schedules, and collaborative team settings, providing stability and defined career paths. Solopreneurs embrace independence, flexibility, and self-direction, managing all aspects of their business while adapting quickly to market changes. These contrasting work styles highlight the trade-off between security and autonomy in professional life.
Table of Comparison
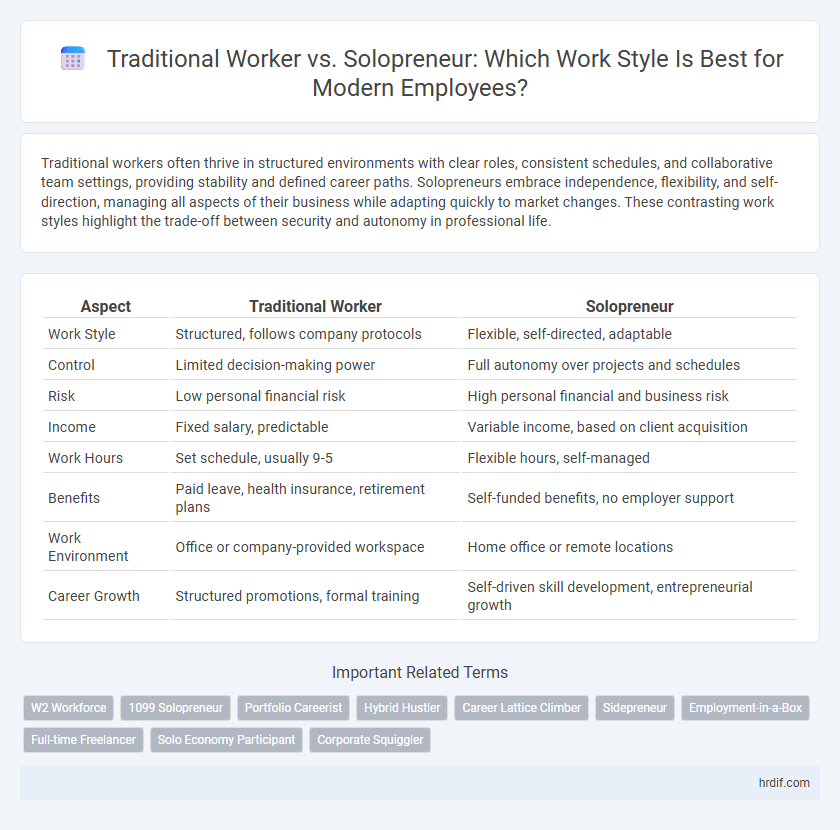
| Aspect | Traditional Worker | Solopreneur |
|---|---|---|
| Work Style | Structured, follows company protocols | Flexible, self-directed, adaptable |
| Control | Limited decision-making power | Full autonomy over projects and schedules |
| Risk | Low personal financial risk | High personal financial and business risk |
| Income | Fixed salary, predictable | Variable income, based on client acquisition |
| Work Hours | Set schedule, usually 9-5 | Flexible hours, self-managed |
| Benefits | Paid leave, health insurance, retirement plans | Self-funded benefits, no employer support |
| Work Environment | Office or company-provided workspace | Home office or remote locations |
| Career Growth | Structured promotions, formal training | Self-driven skill development, entrepreneurial growth |
Defining the Traditional Worker and Solopreneur
The Traditional Worker typically operates within a structured organizational environment, adhering to set schedules, hierarchical management, and defined job roles that prioritize teamwork and consistency. In contrast, a Solopreneur functions independently, managing all aspects of their business from operations to marketing, emphasizing flexibility, autonomy, and personal accountability. This distinction highlights differences in work style, where Traditional Workers benefit from stability and collaboration, while Solopreneurs leverage adaptability and self-direction to drive their entrepreneurial ventures.
Key Differences in Daily Work Structure
Traditional workers follow a structured daily schedule with set hours and defined roles within an organizational hierarchy, emphasizing routine tasks and collaborative environments. Solopreneurs manage flexible work hours, prioritize autonomy, and handle multiple responsibilities across business, marketing, and operations. The contrast in work structures highlights the stability and predictability of traditional employment versus the adaptability and self-reliance required in solopreneurship.
Flexibility and Work-Life Balance Compared
Traditional workers often follow set schedules within structured environments, limiting flexibility but providing clear boundaries between work and personal life. Solopreneurs enjoy high flexibility by controlling their own hours and work locations, enhancing work-life balance but sometimes blurring lines between professional and personal time. Flexibility in solopreneurship supports adapting to personal needs, while traditional roles offer stability and routine that some employees prefer.
Income Stability vs. Income Potential
Traditional workers typically experience stable, predictable income through salaried positions with benefits and consistent paychecks, reducing financial uncertainty. Solopreneurs face variable income streams driven by market demand, client acquisition, and business growth, offering higher earning potential but increased financial risk. Choosing between these work styles depends on prioritizing steady earnings or pursuing flexible, scalable income opportunities.
Career Growth Opportunities: Corporate Ladder vs. Self-Driven
Traditional workers often benefit from structured career growth opportunities within established organizations, with clearly defined corporate ladders and promotion paths. In contrast, solopreneurs drive their own career advancement through self-initiated projects, leveraging flexibility and innovation to create unique business opportunities. These different work styles reflect contrasting approaches to professional development, one relying on hierarchical progression and the other on entrepreneurial self-direction.
Workplace Culture and Social Interaction
Traditional workers often thrive in structured workplace cultures that emphasize teamwork, clear hierarchies, and consistent social interactions, fostering a sense of belonging and collaboration. Solopreneurs prioritize autonomy and flexible work styles, frequently engaging in digital networking and selective in-person interactions to maintain professional relationships. The contrast highlights how traditional employees benefit from routine social environments, whereas solopreneurs tailor their social engagement to suit independent, goal-driven workflows.
Risks and Job Security in Both Paths
Traditional workers benefit from stable income, employer-provided benefits, and clearer legal protections, reducing financial risks and offering higher job security. Solopreneurs face income volatility, self-funding challenges, and the absence of employer-backed benefits, increasing exposure to financial and market risks. Risk management for solopreneurs involves diversifying clients and maintaining emergency funds, whereas traditional employees rely on organizational stability and fixed employment terms.
Skill Development and Learning Approaches
Traditional workers often follow structured learning programs and on-the-job training tailored by employers to enhance specific role-based skills. Solopreneurs prioritize self-directed learning and continuous skill development across multiple domains, leveraging online courses, networking, and real-world problem-solving to adapt quickly. Both approaches influence productivity and career growth, with traditional workers benefiting from organizational support and solopreneurs relying on autonomy and versatility.
Tools and Technology: Corporate Resources vs. DIY Solutions
Traditional workers rely heavily on corporate resources such as enterprise software, IT support, and standardized communication platforms that ensure security and collaboration within large organizations. Solopreneurs opt for DIY solutions, leveraging cloud-based tools, automation apps, and customizable software tailored to their unique business needs for flexibility and cost efficiency. The choice between these work styles influences productivity, with traditional workers benefiting from robust infrastructure and solopreneurs gaining agility through adaptive technologies.
Which Work Style Fits Your Personality and Goals?
Traditional workers typically thrive in structured environments with clear roles, steady schedules, and collaborative teams, making them ideal for those who value stability and predictable career growth. Solopreneurs excel in flexible, autonomous work settings, driven by self-motivation and risk tolerance, aligning well with individuals seeking independence and diverse opportunities. Understanding your preferences for security versus freedom and your adaptability to change helps determine which work style best fits your personality and long-term goals.
Related Important Terms
W2 Workforce
Traditional workers in the W2 workforce typically benefit from structured schedules, stable salaries, and employer-provided benefits, prioritizing job security and consistent work environments. In contrast, solopreneurs embrace flexible work styles with autonomous decision-making and variable income, often sacrificing stability for entrepreneurial freedom and personal brand development.
1099 Solopreneur
Traditional workers often have structured schedules and rely on W-2 employment for consistent income and benefits, while 1099 solopreneurs operate independently, managing their own client relationships and tax obligations with greater flexibility. The 1099 solopreneur model emphasizes autonomy, self-discipline, and diversified revenue streams, appealing to professionals who prioritize control over their work style and financial decisions.
Portfolio Careerist
Traditional workers typically pursue stable, long-term roles within organizations, emphasizing job security and hierarchical advancement, while solopreneurs drive independent ventures requiring multifaceted skill sets and agility. Portfolio careerists blend these models by simultaneously managing multiple income streams and projects, leveraging diverse expertise to maximize flexibility and professional growth.
Hybrid Hustler
Traditional workers thrive in structured environments with defined roles and fixed schedules, while solopreneurs prioritize autonomy and flexibility in managing their workload. Hybrid hustlers blend these approaches by leveraging the stability of traditional employment with the entrepreneurial drive of solopreneurship to maximize productivity and work-life balance.
Career Lattice Climber
Traditional workers often follow a structured career lattice, benefiting from defined roles and upward mobility within organizations, while solopreneurs navigate a more flexible path, focusing on skill diversification and personal brand development. Embracing a career lattice climber mindset, employees prioritize lateral moves and broadening expertise to enhance long-term career growth and adaptability.
Sidepreneur
Traditional workers typically follow structured schedules within established organizations, emphasizing stability and teamwork, while solopreneurs operate independently, prioritizing flexibility and personal brand development; sidepreneurs blend these approaches by maintaining regular employment while growing a side business, leveraging diverse income streams and skill sets to enhance financial security and entrepreneurial experience. This hybrid work style fosters resilience in dynamic markets and supports gradual transition toward full entrepreneurship.
Employment-in-a-Box
Traditional workers benefit from structured environments with defined roles and steady income, while solopreneurs embrace autonomy and flexibility, managing all aspects of their business independently. Employment-in-a-Box solutions streamline solopreneurs' operations by offering integrated tools for payroll, taxes, and compliance, enabling focus on growth without administrative burdens.
Full-time Freelancer
Traditional workers typically operate within structured office environments, adhering to fixed schedules and hierarchical management, whereas full-time freelancers function as solopreneurs who manage their own projects, clients, and deadlines independently. Full-time freelancers prioritize flexibility, self-motivation, and diversified income streams, leveraging digital platforms to maintain consistent work without long-term employer commitments.
Solo Economy Participant
Traditional workers often have structured schedules and rely on established employer support systems, while solopreneurs thrive on autonomy and self-driven project management. Participating in the solo economy, solopreneurs leverage digital tools and flexible work hours to maximize productivity and income potential independently.
Corporate Squiggler
Traditional workers thrive in structured environments with clear hierarchies and consistent routines, benefiting from defined roles and team collaboration within corporate settings. Solopreneurs prioritize autonomy and flexibility, often managing multiple responsibilities independently while driving personal brand growth, a contrast highlighted by the Corporate Squiggler's preference for stability and predictable workflows.
Traditional Worker vs Solopreneur for work style Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com