Backend development provides full control over server infrastructure and customization, allowing for tailored scalability solutions but requires ongoing maintenance and resource management. Serverless development offers automatic scaling and reduced operational overhead by delegating infrastructure management to cloud providers, enabling rapid deployment of scalable services. Choosing between these approaches depends on the project's complexity, control requirements, and desired speed of scaling.
Table of Comparison
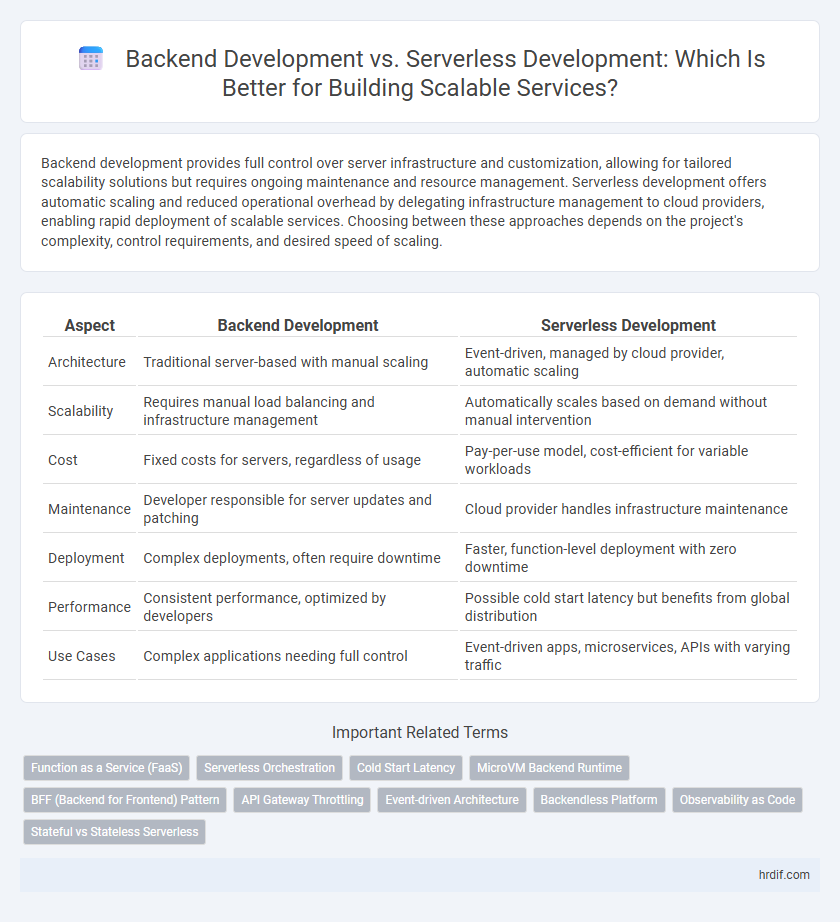
| Aspect | Backend Development | Serverless Development |
|---|---|---|
| Architecture | Traditional server-based with manual scaling | Event-driven, managed by cloud provider, automatic scaling |
| Scalability | Requires manual load balancing and infrastructure management | Automatically scales based on demand without manual intervention |
| Cost | Fixed costs for servers, regardless of usage | Pay-per-use model, cost-efficient for variable workloads |
| Maintenance | Developer responsible for server updates and patching | Cloud provider handles infrastructure maintenance |
| Deployment | Complex deployments, often require downtime | Faster, function-level deployment with zero downtime |
| Performance | Consistent performance, optimized by developers | Possible cold start latency but benefits from global distribution |
| Use Cases | Complex applications needing full control | Event-driven apps, microservices, APIs with varying traffic |
Understanding Backend Development: Core Concepts
Backend development involves building and maintaining the server, database, and application logic that power scalable services. Key concepts include API integration, database management, authentication, and server-side scripting, which enable reliable data processing and seamless client-server communication. Understanding these fundamentals ensures efficient resource allocation, performance optimization, and robust system architecture for scalable backend solutions.
Defining Serverless Development: How It Works
Serverless development allows developers to build and run applications without managing server infrastructure by automatically handling scalable execution through cloud provider services such as AWS Lambda or Azure Functions. Backend development traditionally requires provisioning, configuring, and maintaining servers, which can limit scalability and increase operational overhead. Serverless architecture dynamically allocates resources on demand, ensuring applications respond efficiently to varying workloads and scale seamlessly without manual intervention.
Architectural Differences: Backend vs Serverless
Backend development relies on traditional server-based architecture where applications run on dedicated or virtual servers, providing full control over the environment, scalability, and resource management. Serverless development abstracts server management by using cloud provider-managed services and functions that automatically scale based on demand, eliminating the need for infrastructure provisioning. The key architectural difference lies in backend development's focus on persistent server instances versus serverless development's event-driven execution and inherent scalability through stateless function invocation.
Scalability Challenges: Traditional Backend Approaches
Traditional backend development often struggles with scalability due to fixed server capacity and complex infrastructure management, which can lead to performance bottlenecks under high traffic. Scaling typically requires manual intervention, such as provisioning additional servers or load balancers, increasing operational costs and response times. These challenges highlight the limitations of traditional backend approaches when building scalable services that demand rapid and seamless resource scaling.
Serverless Scalability: Automatic Resource Management
Serverless development excels in scalability by leveraging automatic resource management, dynamically allocating compute power based on real-time demand without manual intervention. This approach eliminates the need for provisioning or managing servers, enabling seamless scaling from zero to peak traffic levels with minimal latency. Backend development often requires pre-planned infrastructure scaling, whereas serverless platforms like AWS Lambda or Azure Functions handle scaling transparently, optimizing cost and performance for scalable services.
Cost Considerations: Backend vs Serverless Deployment
Backend development often requires upfront investment in server infrastructure and ongoing maintenance costs, which can increase with scaling demands. Serverless deployment offers a pay-as-you-go pricing model that reduces operational expenses by charging based on actual usage, minimizing idle resource costs. However, high traffic applications may lead to increased costs in serverless environments due to invocation rates and execution time, making cost analysis crucial when choosing between backend and serverless architectures for scalable services.
Performance and Latency: Comparing Both Solutions
Backend development with dedicated servers offers consistent performance by allowing direct control over resource allocation and server optimization, reducing latency in data processing and response times. Serverless development provides automatic scaling and cost efficiency but can introduce cold start latency, impacting performance during sudden traffic spikes. For high-performance and low-latency scalable services, backend development ensures predictable resource management, whereas serverless is suitable for variable workloads with fluctuating demands.
Security Implications in Backend and Serverless Models
Backend development requires rigorous security measures such as access control, data encryption, and regular patching to mitigate risks from direct server management and potential vulnerabilities in application code. Serverless development shifts much of the security responsibility to the cloud provider, reducing the attack surface but introducing challenges like function-level permissions, secure API gateways, and managing third-party dependencies. Both models demand stringent identity and access management (IAM) policies, but serverless architectures benefit from built-in provider safeguards while facing unique risks like function event data injection and cold start vulnerabilities.
Career Paths: Skills Required for Backend vs Serverless Roles
Backend development careers demand proficiency in languages like Java, Python, or Ruby, along with expertise in server management, databases, and API design. Serverless development roles prioritize skills in cloud platforms such as AWS Lambda, Azure Functions, or Google Cloud Functions, emphasizing event-driven architecture, microservices, and automation. Mastery of containerization and DevOps principles benefits both paths, enhancing scalability and deployment efficiency in modern service infrastructures.
Choosing the Right Approach: When to Use Backend or Serverless
Backend development offers granular control and customization for scalable services, making it ideal when complex logic, persistent connections, or specific infrastructure configurations are required. Serverless development excels in automatic scaling and reducing operational overhead, best suited for event-driven workloads and unpredictable traffic patterns. Evaluate application needs for state management, latency tolerance, and cost efficiency to determine the optimal approach between backend and serverless solutions.
Related Important Terms
Function as a Service (FaaS)
Backend development using traditional server-based architectures offers greater control over infrastructure but often requires extensive provisioning and scaling efforts, whereas serverless development, particularly Function as a Service (FaaS), enables automatic scaling and event-driven execution without managing servers. FaaS platforms like AWS Lambda and Azure Functions optimize resource usage and costs by running discrete functions in response to specific triggers, making them ideal for scalable, granular backend services.
Serverless Orchestration
Serverless orchestration enables scalable backend services by automating workflows across distributed cloud functions without managing servers, enhancing efficiency and reducing operational overhead. Backend development traditionally requires provisioning and maintaining infrastructure, whereas serverless orchestration leverages event-driven architecture to dynamically scale resources based on demand.
Cold Start Latency
Backend development using traditional server infrastructure often experiences lower cold start latency due to persistent server availability, enabling faster response times for scalable services. Serverless development, while offering automatic scaling and simplified management, can suffer from higher cold start latency because functions spin up on demand, potentially delaying responses during initial requests.
MicroVM Backend Runtime
MicroVM backend runtimes provide lightweight, secure, and fast execution environments that enhance scalability for backend development by minimizing overhead and enabling rapid resource provisioning. Serverless development leverages these runtimes to achieve efficient scaling without managing infrastructure, optimizing service responsiveness and cost-effectiveness for dynamic workloads.
BFF (Backend for Frontend) Pattern
Backend Development using the BFF pattern provides tailored APIs for different frontend clients, enhancing performance and maintainability in scalable services. Serverless Development complements this by automatically scaling backend functions, reducing infrastructure management while supporting dynamic BFF implementations.
API Gateway Throttling
Backend development using traditional server-based architecture often requires manual configuration of API gateway throttling to handle request limits and prevent overload, ensuring consistent scalability. Serverless development natively integrates API Gateway throttling, automatically managing concurrency and rate limits to optimize resource usage and maintain high availability in scalable services.
Event-driven Architecture
Backend development leverages traditional server-based frameworks providing full control over infrastructure, while serverless development utilizes event-driven architecture to automatically scale services in response to triggers without managing servers. Event-driven architecture enables backend systems to handle high-throughput, asynchronous events efficiently, reducing latency and improving scalability for cloud-native applications.
Backendless Platform
Backendless Platform streamlines scalable services by combining traditional backend development with serverless architecture, enabling automatic scaling, real-time database management, and integrated API services without manual infrastructure management. Its visual development tools and managed backend environment accelerate deployment while optimizing resource allocation and performance for high-demand applications.
Observability as Code
Backend development with traditional server architectures enables granular control over observability through customizable monitoring tools and infrastructure-level metrics, essential for diagnosing performance in scalable services. Serverless development leverages observability as code to automate and integrate monitoring configurations natively within deployment pipelines, enhancing real-time visibility and operational efficiency at scale.
Stateful vs Stateless Serverless
Backend development traditionally relies on stateful architectures that maintain persistent connections and data across sessions, ensuring complex transaction management and real-time processing; in contrast, serverless development promotes stateless functions that scale automatically by handling discrete, event-driven requests without retaining client state. Emphasizing stateless serverless design enhances scalability and fault tolerance for microservices, while stateful backend systems enable richer interactions requiring maintained context and session information.
Backend Development vs Serverless Development for scalable services. Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com