Certification provides a formal recognition of specific skills and knowledge validated by an authoritative body, often requiring comprehensive assessments and adherence to industry standards. Microcredentials offer targeted, flexible learning achievements that focus on niche skills, making them ideal for quickly adapting to job market demands and enhancing specialized competencies. Both certifications and microcredentials enhance job qualifications, but certifications typically carry more weight in traditional hiring processes, while microcredentials are valued for continuous professional development and skill diversification.
Table of Comparison
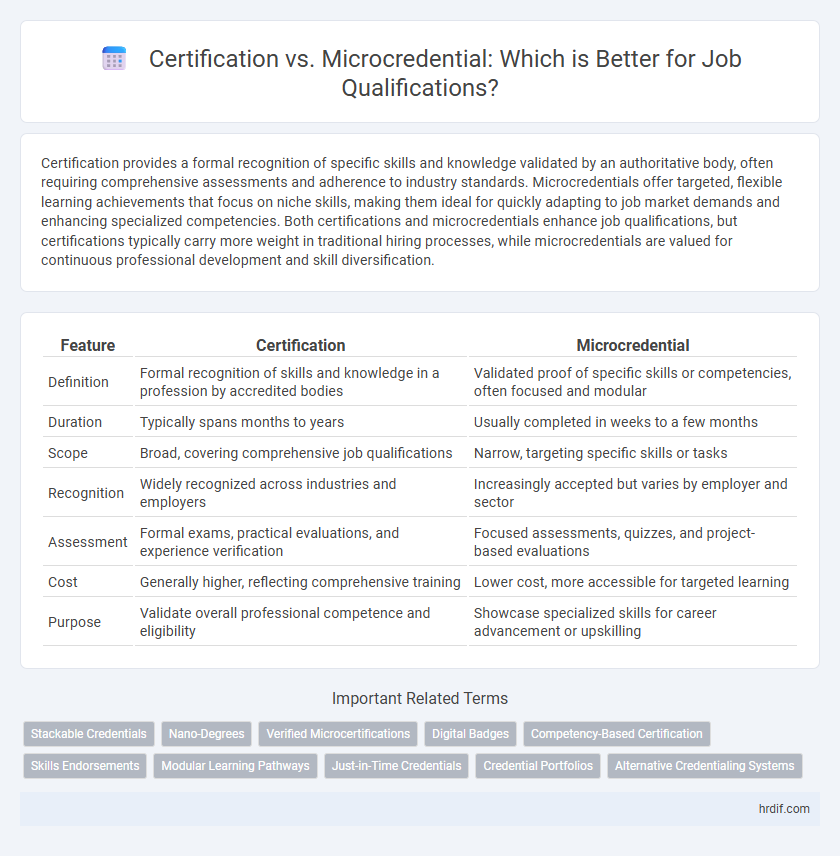
| Feature | Certification | Microcredential |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Formal recognition of skills and knowledge in a profession by accredited bodies | Validated proof of specific skills or competencies, often focused and modular |
| Duration | Typically spans months to years | Usually completed in weeks to a few months |
| Scope | Broad, covering comprehensive job qualifications | Narrow, targeting specific skills or tasks |
| Recognition | Widely recognized across industries and employers | Increasingly accepted but varies by employer and sector |
| Assessment | Formal exams, practical evaluations, and experience verification | Focused assessments, quizzes, and project-based evaluations |
| Cost | Generally higher, reflecting comprehensive training | Lower cost, more accessible for targeted learning |
| Purpose | Validate overall professional competence and eligibility | Showcase specialized skills for career advancement or upskilling |
Understanding Certification and Microcredential: Key Differences
Certification validates comprehensive expertise through a formal process recognized by industry standards, often requiring exams and continual education. Microcredentials target specific skills or competencies, offering flexible, shorter-term proof of proficiency tailored to evolving job requirements. Both serve distinct roles in professional development, with certification emphasizing broad qualification and microcredentials focusing on specialized skills.
Industry Recognition: Certification vs Microcredential
Certification holds stronger industry recognition compared to microcredentials due to its rigorous standards and widespread acceptance by employers and professional bodies. Microcredentials, while flexible and focused on specific skills, often lack the formal validation and comprehensive evaluation processes that certifications undergo. Employers tend to prioritize certifications when assessing job qualifications because they signify verified expertise and adherence to established industry benchmarks.
Depth of Learning: Comprehensive Curricula Compared
Certification programs offer comprehensive curricula designed to provide in-depth knowledge and mastery of subject matter essential for professional standards. Microcredentials focus on specific skills or competencies, delivering targeted learning with less emphasis on broader theoretical foundations. Employers often regard certifications as evidence of thorough expertise, whereas microcredentials validate proficiency in niche areas.
Time Investment: Earning a Certification vs a Microcredential
Certifications typically require a longer time investment, often ranging from several months to over a year, due to comprehensive curricula and rigorous exams, whereas microcredentials can be earned in weeks or a few months through focused, skill-specific coursework. Employers increasingly recognize microcredentials for their agility in reflecting up-to-date expertise, but certifications remain valued for their depth and industry-wide acceptance. Choosing between the two depends on career goals, with certifications supporting long-term qualification and microcredentials enabling rapid upskilling.
Cost Effectiveness: Weighing Certification and Microcredential Expenses
Certification programs typically involve higher upfront costs but offer comprehensive validation of skills recognized across industries, enhancing long-term career prospects. Microcredentials, with lower fees and shorter completion times, provide cost-effective options for targeted skill acquisition and immediate application in specific job roles. Employers increasingly value the flexibility of microcredentials, which deliver focused expertise at a fraction of traditional certification expenses.
Career Advancement Opportunities: Which Opens More Doors?
Certifications often carry greater industry recognition and can lead to higher-paying, long-term career advancement opportunities by validating comprehensive skill sets and expertise. Microcredentials target specific skills and are valued for rapid upskilling or showcasing niche competencies in evolving job markets. Employers prioritize certifications for established roles but increasingly consider microcredentials for specialized or emerging fields, creating diverse pathways for career growth.
Employer Preferences: What Do Recruiters Value?
Employers prioritize certifications over microcredentials for job qualifications due to their recognized industry standards, rigorous assessment criteria, and proven competency validation. Certifications offer comprehensive proof of skill mastery that aligns with organizational requirements, making candidates more attractive during recruitment. Microcredentials, while valuable for specific skills, often lack the depth and widespread acceptance that recruiters rely on for critical role assessments.
Flexibility and Accessibility: Learning Paths Explored
Certifications often involve comprehensive, standardized assessments focusing on industry-recognized skills, while microcredentials provide flexible, modular learning paths tailored for specific competencies. Microcredentials enhance accessibility by allowing professionals to acquire targeted expertise through shorter, more affordable courses without full program commitments. Both options improve job qualifications, but microcredentials prioritize adaptability and continuous learning, supporting evolving career needs and diverse schedules.
Relevance to Emerging Skills and Technologies
Certification programs often provide comprehensive validation of expertise in established industry standards, whereas microcredentials focus on demonstrating proficiency in specific, emerging skills and technologies. Microcredentials offer agility in rapidly evolving fields by allowing professionals to quickly acquire and showcase targeted competencies aligned with the latest market demands. Employers increasingly value microcredentials for their ability to confirm up-to-date knowledge in cutting-edge tools and methodologies essential for job performance.
Choosing the Right Path: Certification or Microcredential for Your Career
Certifications often provide comprehensive validation of expertise in a specific field, recognized by industry standards and employers worldwide. Microcredentials offer targeted skill development for niche areas, enabling quicker, flexible learning aligned with evolving job market demands. Selecting between certification and microcredential depends on career goals, required skill depth, and the value recognized by your industry.
Related Important Terms
Stackable Credentials
Stackable credentials, combining certifications and microcredentials, offer a flexible pathway for job qualifications by allowing learners to accumulate specialized skills progressively. Certifications demonstrate comprehensive mastery in a field, while microcredentials provide targeted expertise, enabling professionals to adapt quickly to evolving industry demands.
Nano-Degrees
Nano-Degrees provide targeted, skill-specific training that complements traditional certifications by offering practical, project-based learning recognized by top employers in tech industries. Unlike broad certifications, Nano-Degrees emphasize immediate job readiness and are often developed in partnership with leading companies, enhancing employability through focused microcredential recognition.
Verified Microcertifications
Verified microcertifications offer targeted skill validation with faster completion times compared to traditional certifications, making them ideal for rapidly evolving job markets. These credentials, backed by trusted institutions, provide employers with reliable evidence of specific competencies, enhancing hiring precision and workforce development.
Digital Badges
Digital badges represent a modern approach to certifications, providing verifiable, microcredential evidence of specific skills and competencies valued by employers in the job market. Unlike traditional certifications, which often require extensive time and resources, digital badges offer flexible, stackable credentials that enhance job qualifications and demonstrate continuous professional development.
Competency-Based Certification
Competency-based certification validates specific skills and expertise through rigorous assessments directly tied to job performance, offering a more recognized and industry-aligned qualification than microcredentials. While microcredentials highlight targeted knowledge in niche areas, competency-based certifications provide comprehensive proof of capability essential for career advancement and employer trust.
Skills Endorsements
Certifications provide formal recognition of comprehensive industry standards and expertise, while microcredentials focus on validating specific skills endorsements tailored to evolving job requirements. Employers increasingly value microcredentials for their ability to highlight targeted competencies and practical skills relevant to specialized roles.
Modular Learning Pathways
Certification offers comprehensive validation of professional competencies through structured assessments, whereas microcredentials provide targeted recognition for specific skills within modular learning pathways, enabling flexible, stackable achievements tailored to evolving job requirements. Modular learning pathways facilitate progressive skill acquisition by linking microcredentials to broader certifications, enhancing career mobility and personalized professional development.
Just-in-Time Credentials
Just-in-time credentials like microcredentials offer flexible, targeted skill validation that aligns closely with evolving job market demands, enabling professionals to rapidly demonstrate relevant competencies. Certifications provide comprehensive, standardized recognition of expertise but often require longer preparation periods, making microcredentials more adaptive for immediate qualification needs.
Credential Portfolios
Certification typically represents a formal, industry-recognized qualification demonstrating comprehensive expertise, while microcredentials offer targeted, skill-specific validation suited for agile learning paths. Credential portfolios effectively combine both certifications and microcredentials, providing a holistic view of a candidate's qualifications and enhancing job market competitiveness.
Alternative Credentialing Systems
Certification offers formal recognition of industry-specific skills validated by accredited bodies, while microcredentials provide flexible, bite-sized learning achievements tailored to emerging job roles and technologies. Alternative credentialing systems like digital badges and nano-degrees enhance workforce agility by enabling rapid skill acquisition and verifiable accomplishments aligned with evolving career demands.
Certification vs Microcredential for job qualifications Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com