Self-assessment in an appraisal allows employees to reflect on their own performance and identify strengths and areas for improvement, fostering personal accountability. Peer assessment provides diverse perspectives and constructive feedback from colleagues who closely observe daily work interactions, enhancing the evaluation's accuracy. Combining both methods creates a balanced appraisal process that promotes self-awareness and collaborative growth.
Table of Comparison
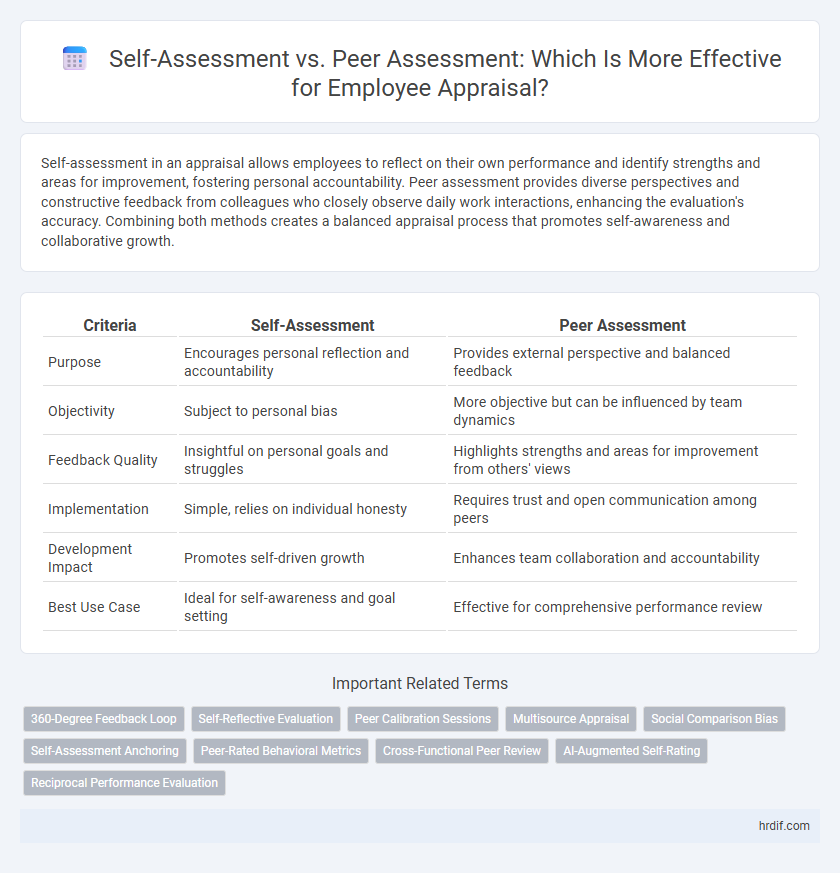
| Criteria | Self-Assessment | Peer Assessment |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Encourages personal reflection and accountability | Provides external perspective and balanced feedback |
| Objectivity | Subject to personal bias | More objective but can be influenced by team dynamics |
| Feedback Quality | Insightful on personal goals and struggles | Highlights strengths and areas for improvement from others' views |
| Implementation | Simple, relies on individual honesty | Requires trust and open communication among peers |
| Development Impact | Promotes self-driven growth | Enhances team collaboration and accountability |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for self-awareness and goal setting | Effective for comprehensive performance review |
Understanding Self-Assessment in Appraisal
Self-assessment in appraisal empowers employees to reflect critically on their own performance, identifying strengths and areas for improvement using predefined criteria aligned with organizational goals. This introspective process enhances self-awareness, promotes accountability, and supports personalized development plans by allowing individuals to set realistic benchmarks and measure progress over time. Integrating self-assessment with quantitative performance metrics provides a comprehensive understanding of employee contributions and fosters continuous professional growth.
The Value of Peer Assessment in Performance Reviews
Peer assessment provides a unique perspective by offering insights into an employee's collaborative skills, work ethic, and interpersonal dynamics that self-assessments may overlook. It enhances performance reviews with diverse feedback, promoting a more comprehensive and objective evaluation of strengths and areas for improvement. Incorporating peer assessments leads to increased accountability and fosters a culture of continuous learning within organizations.
Key Differences Between Self and Peer Assessment
Self-assessment in appraisal involves individuals evaluating their own performance based on personal insights and set objectives, emphasizing self-awareness and responsibility. Peer assessment, on the other hand, gathers evaluations from colleagues, offering diverse perspectives and fostering collaborative feedback. Key differences include the subjectivity of self-assessment versus the broader viewpoint of peer assessment, and the potential for bias in personal evaluation contrasted with the checks and balances provided by multiple peer inputs.
Benefits of Self-Assessment for Career Growth
Self-assessment in appraisal empowers employees to identify their strengths and areas for improvement, fostering greater self-awareness and personal accountability. This reflective process promotes goal setting aligned with career aspirations, enhancing motivation and targeted skill development. By actively engaging in self-evaluation, individuals gain clarity on their progress, which supports continuous professional growth and improved performance outcomes.
Advantages of Peer Assessment in the Workplace
Peer assessment in the workplace enhances appraisal accuracy by incorporating diverse perspectives, reducing individual bias commonly found in self-assessment. It fosters stronger team collaboration and accountability, as employees receive constructive feedback from colleagues who directly observe their performance. Implementing peer assessment boosts employee engagement and helps identify skill gaps more effectively, driving targeted professional development.
Common Challenges in Self and Peer Appraisals
Common challenges in self-assessment and peer assessment for appraisals include inherent bias, where individuals may either overestimate or underestimate their performance, impacting accuracy. In peer assessments, issues like favoritism or interpersonal conflicts can distort evaluations, while self-assessments may suffer from lack of objectivity and critical self-reflection. Both methods require clear criteria and training to ensure consistency and fairness in performance appraisals.
Strategies to Enhance Self-Appraisal Accuracy
To enhance self-appraisal accuracy, individuals should employ structured reflection techniques such as using standardized rating scales aligned with performance criteria and maintaining detailed performance logs to capture real-time achievements and challenges. Incorporating regular feedback from peers and supervisors can calibrate self-perceptions, reducing biases and fostering realistic self-evaluations. Utilizing goal-setting frameworks like SMART objectives helps in tracking progress objectively, ensuring that self-assessments reflect measurable outcomes and areas for development.
Improving Objectivity in Peer Assessment
Self-assessment allows individuals to reflect on their own performance, promoting personal insight, but it often lacks external validation. Peer assessment introduces diverse perspectives that enhance fairness and reduce bias, improving objectivity in performance appraisals. Incorporating structured criteria and anonymous feedback in peer reviews further strengthens the reliability of appraisal outcomes.
Integrating Self and Peer Assessments for Balanced Appraisals
Integrating self-assessment and peer assessment in appraisals enhances evaluation accuracy by combining personal insights with external perspectives, fostering a more comprehensive understanding of performance. This balanced approach mitigates individual biases, supports developmental feedback, and encourages accountability among employees. Organizations adopting this method benefit from improved employee engagement and more data-driven decision-making in talent management.
Best Practices for Effective Appraisal Systems
Effective appraisal systems integrate self-assessment and peer assessment to enhance accuracy and developmental feedback. Best practices include using structured criteria aligned with organizational goals, promoting honest communication, and training employees on unbiased evaluation methods. Combining these assessments fosters greater employee engagement and supports continuous performance improvement.
Related Important Terms
360-Degree Feedback Loop
Self-assessment in appraisal empowers employees to reflect on their performance, while peer assessment provides diverse perspectives within the 360-degree feedback loop, enhancing accuracy and depth. Integrating both methods fosters comprehensive evaluations, promotes continuous development, and boosts organizational transparency.
Self-Reflective Evaluation
Self-reflective evaluation in self-assessment empowers employees to critically analyze their performance, strengths, and growth areas, fostering personal accountability and deeper insight into their work. This reflective process complements peer assessment by providing a balanced perspective, integrating individual self-awareness with external feedback to enhance overall appraisal accuracy.
Peer Calibration Sessions
Peer calibration sessions enhance appraisal accuracy by aligning evaluations through collective discussions, reducing individual bias in peer assessments. This process ensures consistent performance standards across teams, making peer assessments more reliable than isolated self-assessments.
Multisource Appraisal
Multisource appraisal integrates self-assessment and peer assessment to provide a comprehensive evaluation by combining the individual's self-perceptions with colleagues' objective feedback. This approach enhances accuracy and reduces bias, delivering a balanced view of performance and development needs in organizational appraisals.
Social Comparison Bias
Self-assessment in appraisals often suffers from social comparison bias, as individuals may inaccurately rate their performance relative to peers to protect self-esteem or boost status. Peer assessment can mitigate this bias by offering diverse perspectives, although it may introduce other biases; combining both methods typically enhances appraisal accuracy and fairness.
Self-Assessment Anchoring
Self-assessment anchoring in appraisal enables individuals to critically evaluate their own performance using specific, measurable criteria, fostering greater self-awareness and accountability. This method enhances accuracy by reducing bias often present in peer assessments and supports personalized development plans grounded in authentic self-reflection.
Peer-Rated Behavioral Metrics
Peer-rated behavioral metrics provide a more objective and comprehensive evaluation in appraisals by capturing diverse perspectives on an employee's teamwork, communication, and adaptability skills. These metrics enhance accuracy in identifying development areas compared to self-assessment, which often suffers from bias and limited self-awareness.
Cross-Functional Peer Review
Cross-functional peer review enhances appraisal accuracy by incorporating diverse perspectives from multiple departments, leading to a more comprehensive evaluation of an employee's performance. Self-assessment offers personal insight but lacks the objectivity provided by cross-functional feedback, which identifies strengths and areas for improvement across different skill sets and operational contexts.
AI-Augmented Self-Rating
AI-augmented self-rating in appraisal leverages machine learning algorithms to provide employees with data-driven insights and objective performance metrics, enhancing the accuracy and depth of self-assessments. Integrating AI tools allows for real-time feedback comparison against peer benchmarks, reducing biases commonly found in traditional self- and peer assessment methods.
Reciprocal Performance Evaluation
Reciprocal performance evaluation integrates self-assessment and peer assessment to provide a comprehensive appraisal by combining individual insights with collaborative feedback, enhancing accuracy in identifying strengths and areas for improvement. This balanced approach fosters mutual accountability, encourages continuous development, and promotes a transparent performance culture within organizations.
Self-Assessment vs Peer Assessment for Appraisal Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com