Goal setting in appraisal focuses on defining clear, measurable objectives tailored to individual performance and development. The OKR (Objectives and Key Results) methodology emphasizes alignment of personal goals with broader organizational outcomes through specific, quantifiable key results. Integrating OKRs into appraisal processes enhances transparency, accountability, and continuous progress tracking, driving more strategic employee growth.
Table of Comparison
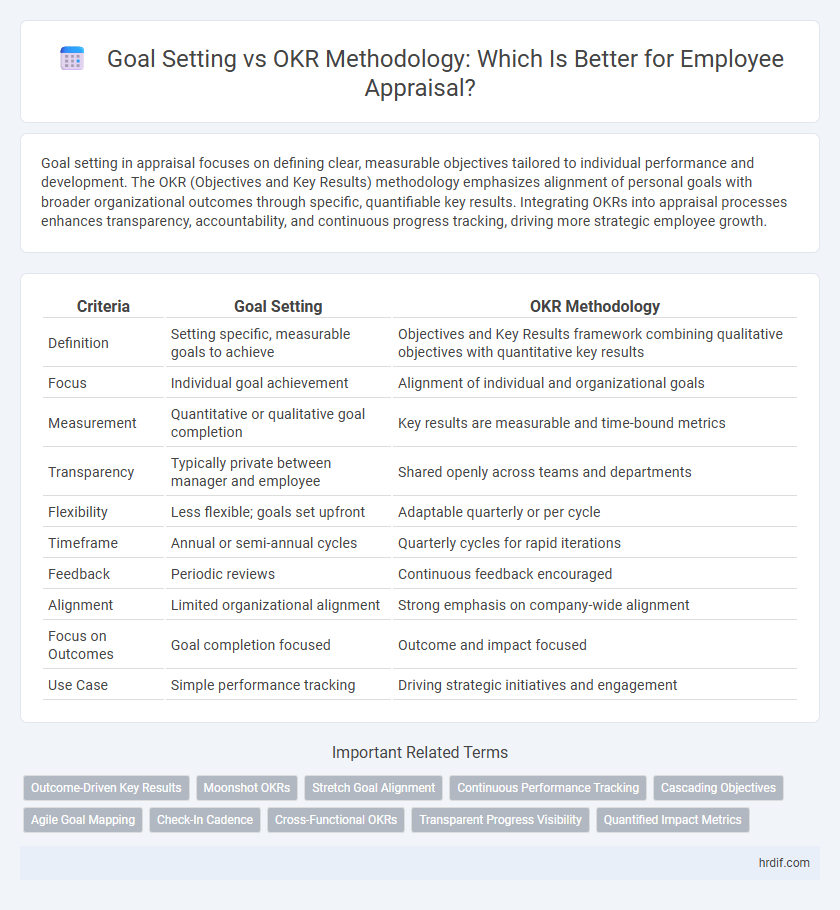
| Criteria | Goal Setting | OKR Methodology |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Setting specific, measurable goals to achieve | Objectives and Key Results framework combining qualitative objectives with quantitative key results |
| Focus | Individual goal achievement | Alignment of individual and organizational goals |
| Measurement | Quantitative or qualitative goal completion | Key results are measurable and time-bound metrics |
| Transparency | Typically private between manager and employee | Shared openly across teams and departments |
| Flexibility | Less flexible; goals set upfront | Adaptable quarterly or per cycle |
| Timeframe | Annual or semi-annual cycles | Quarterly cycles for rapid iterations |
| Feedback | Periodic reviews | Continuous feedback encouraged |
| Alignment | Limited organizational alignment | Strong emphasis on company-wide alignment |
| Focus on Outcomes | Goal completion focused | Outcome and impact focused |
| Use Case | Simple performance tracking | Driving strategic initiatives and engagement |
Understanding Goal Setting in Performance Appraisal
Goal setting in performance appraisal involves defining clear, measurable objectives that align employee efforts with organizational priorities, enhancing focus and accountability. Unlike the OKR methodology, which emphasizes ambitious, qualitative objectives and key results to drive innovation, traditional goal setting often relies on specific, achievable targets linked directly to individual performance metrics. Understanding the distinctions helps organizations tailor appraisal systems to balance motivation, clarity, and strategic impact effectively.
What is OKR Methodology?
OKR (Objectives and Key Results) methodology is a goal-setting framework that aligns individual performance with organizational objectives through measurable key results. It emphasizes transparency, measurable outcomes, and frequent progress tracking, making it more dynamic and adaptable than traditional goal-setting methods. OKRs foster accountability and continuous improvement by setting ambitious yet achievable targets reviewed regularly during the appraisal process.
Key Differences Between Goal Setting and OKRs
Goal setting typically involves defining specific, measurable, and time-bound objectives focused on individual or team performance, while the OKR (Objectives and Key Results) methodology emphasizes ambitious, qualitative objectives paired with quantifiable key results to track progress. Unlike traditional goal setting, OKRs promote transparency, alignment across teams, and iterative progress reviews, enabling real-time adjustments and continuous improvement. Key differences include the structured cadence in OKRs and their focus on stretch goals that drive innovation, contrasting with the often static and easily achievable goals in conventional appraisal systems.
Benefits of Traditional Goal Setting for Appraisals
Traditional goal setting for appraisals provides clear, specific targets that enhance employee focus and accountability. It allows for straightforward progress tracking and performance measurement against predefined criteria. This method fosters consistency and clarity in evaluation, supporting structured development and reward systems within organizations.
Advantages of Using OKR Methodology in Appraisals
OKR methodology in appraisals enhances clarity by aligning individual goals with measurable key results, driving focused performance evaluation. It promotes transparency and continuous feedback, enabling timely adjustments and fostering employee engagement throughout the appraisal cycle. The measurable nature of OKRs supports data-driven decisions, improving the accuracy and fairness of performance assessments.
Challenges in Implementing Goal Setting and OKRs
Implementing traditional goal setting often faces challenges such as lack of alignment with overall business objectives and difficulty in tracking progress consistently. The OKR methodology encounters issues like setting overly ambitious objectives that can demotivate employees when unmet and the complexity of maintaining frequent check-ins and updates. Both methods require robust communication, clear performance metrics, and continuous management support to ensure effective appraisal outcomes.
Measuring Employee Performance: Goals vs. OKRs
Measuring employee performance through traditional goal setting often relies on predefined, static objectives that may lack alignment with broader business outcomes. In contrast, the OKR (Objectives and Key Results) methodology emphasizes setting ambitious, transparent objectives paired with measurable key results, driving continuous performance tracking and adaptability. OKRs foster clearer accountability and strategic focus, enabling more dynamic and outcome-oriented appraisals compared to conventional goal-setting approaches.
Aligning Individual Objectives with Organizational Strategy
Goal setting techniques establish clear, measurable targets tailored to individual roles, enabling focused performance assessment. OKR (Objectives and Key Results) methodology emphasizes transparency and alignment by cascading organizational priorities into specific, quantifiable objectives at all levels. Integrating OKRs in appraisals ensures that individual contributions directly support strategic goals, fostering cohesive progress across departments.
Best Practices for Integrating OKRs into Appraisal Systems
Integrating OKRs into appraisal systems enhances performance tracking by aligning individual objectives with company goals, fostering transparency and continuous feedback. Best practices include setting clear, measurable OKRs, conducting regular check-ins to assess progress, and using results to inform performance evaluations rather than annual reviews alone. This approach drives employee engagement and ensures appraisal outcomes reflect real-time achievements and growth areas.
Choosing the Right Approach: Goal Setting or OKRs for Your Organization
Selecting between traditional goal setting and OKR methodology depends on your organization's need for flexibility and alignment. Goal setting provides clear, measurable targets ideal for individual performance tracking, while OKRs (Objectives and Key Results) emphasize ambitious, transparent objectives that drive cross-functional collaboration and continuous progress. Implementing OKRs fosters agility and innovation, making them suitable for dynamic environments where iterative assessment and adaptation are critical for success.
Related Important Terms
Outcome-Driven Key Results
Goal setting in appraisals establishes clear performance targets, while the OKR methodology emphasizes Outcome-Driven Key Results, linking measurable outcomes directly to business objectives. OKRs foster continuous alignment, transparency, and accountability by focusing on impactful, data-driven progress rather than just task completion.
Moonshot OKRs
Goal setting in appraisal provides clear, achievable targets, but Moonshot OKRs push boundaries with ambitious, transformative objectives that drive innovation and exponential growth. Moonshot OKRs prioritize breakthrough results over incremental progress, fostering a culture of bold experimentation and high-impact outcomes in performance evaluation.
Stretch Goal Alignment
Stretch goal alignment in appraisal is enhanced through OKR methodology by clearly defining measurable Objectives and Key Results that drive ambitious performance targets, compared to traditional goal setting which often lacks specificity and measurable outcomes, leading to less effective performance tracking and motivation. OKRs foster transparency and continual progress assessment, ensuring stretch goals are strategically aligned with organizational priorities and individual growth.
Continuous Performance Tracking
Goal setting provides clear, measurable targets for employee appraisal, but the OKR methodology enhances continuous performance tracking by promoting frequent check-ins and real-time progress updates. This iterative approach fosters agility and alignment with organizational priorities, ensuring objectives remain relevant throughout the appraisal period.
Cascading Objectives
Goal setting in appraisal emphasizes individual targets aligned with broader company aims, while the OKR methodology leverages cascading objectives to create transparent, measurable goals that link team and personal performance directly to organizational priorities. Cascading objectives in OKRs enhance accountability and strategic alignment by breaking down overarching goals into specific, trackable results at every level of the organization.
Agile Goal Mapping
Agile Goal Mapping enhances appraisal effectiveness by integrating the flexibility of OKR methodology with traditional goal setting, enabling continuous alignment of individual objectives to organizational priorities. OKRs promote transparency and measurable outcomes, fostering real-time feedback loops that optimize performance evaluation compared to static goal setting methods.
Check-In Cadence
Goal setting typically involves annual or semi-annual check-ins, which may delay real-time feedback and adjustment, whereas the OKR methodology employs quarterly or even monthly check-ins to ensure continuous alignment and agile performance tracking. Frequent OKR check-ins foster dynamic communication, immediate problem-solving, and agile goal refinement that enhances employee engagement and drives measurable outcomes.
Cross-Functional OKRs
Goal setting in appraisals typically involves setting individual targets, while the OKR (Objectives and Key Results) methodology emphasizes measurable outcomes aligned with broader company goals, promoting transparency and accountability. Cross-Functional OKRs enhance collaboration by integrating diverse team objectives, driving innovation and unified progress across departments during performance evaluations.
Transparent Progress Visibility
Goal setting provides a clear framework for individual objectives, but the OKR methodology enhances transparent progress visibility by aligning measurable key results with organizational goals and enabling real-time tracking of performance. This transparency fosters accountability and motivates continuous improvement throughout the appraisal cycle.
Quantified Impact Metrics
Goal setting in appraisals typically involves setting broad, qualitative objectives, whereas the OKR (Objectives and Key Results) methodology emphasizes quantifiable impact metrics to measure progress and success precisely. Incorporating OKRs enables organizations to track specific, data-driven outcomes such as revenue growth, customer satisfaction scores, and productivity increases, enhancing the appraisal's effectiveness in driving performance improvements.
Goal setting vs OKR methodology for appraisal. Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com