Choosing between a university degree and a micro-credential depends on career goals and industry requirements. University degrees offer comprehensive knowledge, broad skill sets, and are often preferred for roles requiring deep theoretical understanding. Micro-credentials provide targeted, practical skills and flexibility, making them ideal for professionals seeking quick upskilling or specialization without the time commitment of a full degree.
Table of Comparison
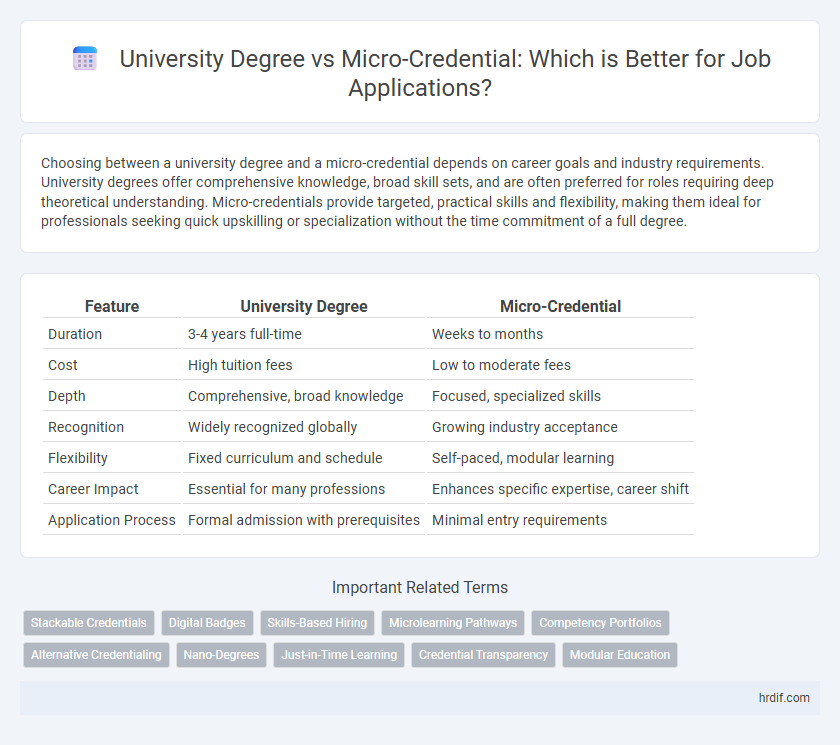
| Feature | University Degree | Micro-Credential |
|---|---|---|
| Duration | 3-4 years full-time | Weeks to months |
| Cost | High tuition fees | Low to moderate fees |
| Depth | Comprehensive, broad knowledge | Focused, specialized skills |
| Recognition | Widely recognized globally | Growing industry acceptance |
| Flexibility | Fixed curriculum and schedule | Self-paced, modular learning |
| Career Impact | Essential for many professions | Enhances specific expertise, career shift |
| Application Process | Formal admission with prerequisites | Minimal entry requirements |
Defining University Degrees and Micro-Credentials
University degrees are comprehensive academic programs typically spanning several years and culminating in a bachelor's, master's, or doctoral qualification recognized by accredited institutions. Micro-credentials are focused, short-term certifications designed to validate specific skills or competencies, often delivered through online platforms or professional development courses. Both serve different purposes within applications, with degrees providing broad foundational knowledge and micro-credentials offering targeted expertise aligned with evolving industry demands.
Evaluating Employer Preferences: Degrees vs Micro-Credentials
Employers increasingly weigh both university degrees and micro-credentials when evaluating candidates, emphasizing relevant skills and practical experience over traditional qualifications alone. Micro-credentials offer targeted expertise and flexibility, appealing to industries seeking up-to-date competencies and rapid adaptability. University degrees still hold value for foundational knowledge and signaling comprehensive education but face competition from specialized, scalable credentials in hiring decisions.
Cost-Benefit Analysis: Investment in Education
Micro-credentials offer a cost-effective alternative to traditional university degrees by providing targeted skills with lower tuition fees and shorter completion times, enabling faster entry into the workforce. University degrees, although more expensive and time-consuming, often deliver comprehensive knowledge and higher long-term earning potential through established recognition. Evaluating the return on investment requires assessing individual career goals, industry demands, and the value employers place on credentials when considering education costs and benefits.
Time to Completion: Fast-Tracking Career Opportunities
Micro-credentials offer significantly faster completion times compared to traditional university degrees, enabling learners to acquire targeted skills within weeks or months rather than years. This accelerated timeline facilitates quicker entry or advancement in specific career paths by aligning education with emerging industry demands. Employers increasingly recognize micro-credentials for their practicality and relevance, making them a strategic choice for fast-tracking professional growth.
Industry Recognition and Accreditation Differences
University degrees typically hold widespread industry recognition due to their comprehensive accreditation by regional and national educational bodies, ensuring a standardized level of academic rigor. Micro-credentials, while growing in popularity, often lack the same formal accreditation but gain recognition through endorsement by specific industry partners or professional organizations. Employers may prefer degrees for roles requiring foundational knowledge, but micro-credentials are valued for their targeted skills and quicker adaptability to emerging industry standards.
Practical Skills Acquisition: Micro-Credentials vs Traditional Learning
Micro-credentials emphasize practical skills acquisition through focused, competency-based modules tailored to current industry demands, offering learners rapid application and immediate relevance. Traditional university degrees provide comprehensive theoretical foundations but may lack the agility to update curricula in response to evolving job market requirements. Consequently, micro-credentials deliver targeted skill sets that enhance employability and adaptability in dynamic professional environments.
Flexibility and Accessibility of Learning Paths
Micro-credentials offer greater flexibility and accessibility in learning paths compared to traditional university degrees, allowing learners to acquire specific skills through short, focused courses. These credentials can be earned online, asynchronously, and at a lower cost, making education more accessible to working professionals and non-traditional students. Universities increasingly complement degree programs with micro-credentials to cater to diverse learner needs and rapidly evolving job market demands.
Impact on Career Advancement and Salary Prospects
University degrees typically provide comprehensive knowledge and are highly valued by employers, resulting in stronger career advancement opportunities and higher salary prospects over time. Micro-credentials offer targeted skills and quicker completion, appealing to industry-specific roles and enabling immediate application of new competencies, but may not carry the same long-term impact on salary growth. Combining both educational paths can optimize professional development by balancing broad foundational knowledge with specialized expertise.
Case Studies: Success Stories of Degree and Micro-Credential Holders
Case studies reveal that university degree holders often secure advanced positions in specialized fields due to their comprehensive education, while micro-credential holders demonstrate rapid skill acquisition and adaptability, leading to immediate job opportunities in emerging industries. Research highlights that degree holders benefit from deep theoretical knowledge and broader career prospects, whereas micro-credential recipients excel in practical, targeted competencies that meet specific employer demands. Employers increasingly recognize micro-credentials for their role in continuous learning and workforce agility, complementing traditional degrees in various application contexts.
Future Trends: The Evolving Landscape of Job Applications
Employers increasingly prioritize micro-credentials that demonstrate specific skills and real-world experience over traditional university degrees in job applications. The rise of digital badges and online certification platforms reflects a shift towards flexible, skills-based hiring practices. Future job application trends emphasize continuous learning and verification of competencies through micro-credentials to meet rapidly evolving industry demands.
Related Important Terms
Stackable Credentials
Stackable credentials, such as micro-credentials, offer flexible and targeted skill development that can be accumulated over time to complement or substitute traditional university degrees in applications. Employers increasingly recognize these modular qualifications for their relevance to specific job roles, enabling applicants to demonstrate up-to-date competencies alongside or instead of comprehensive academic credentials.
Digital Badges
Digital badges serve as micro-credentials that validate specific skills and competencies acquired through short-term, focused learning experiences, offering a flexible and stackable alternative to traditional university degrees. These digital credentials enhance application portfolios by providing verifiable, skill-based evidence that meets employer demands for continuous upskilling and real-time proof of expertise.
Skills-Based Hiring
Skills-based hiring increasingly favors micro-credentials over traditional university degrees by emphasizing verified competencies and practical expertise directly relevant to job performance. Employers prioritize applicants with specific, demonstrable skills acquired through targeted micro-credential programs, which offer faster, more flexible pathways to workforce readiness.
Microlearning Pathways
Micro-credential programs offer targeted, flexible microlearning pathways that enable learners to acquire specific skills and competencies efficiently unlike traditional university degrees, which require longer time commitments. These modular credentials, often industry-recognized, enhance workforce readiness and provide continuous learning opportunities aligned with evolving job market demands.
Competency Portfolios
Competency portfolios in micro-credentials offer targeted skill validation and flexibility, enabling applicants to showcase specific abilities relevant to job requirements more effectively than traditional university degrees. Employers increasingly value these portfolios as concrete evidence of practical expertise, streamlining the application process and enhancing candidate differentiation.
Alternative Credentialing
Micro-credentials offer targeted skill validation and faster completion times compared to traditional university degrees, making them ideal for rapidly evolving industries and lifelong learning. Alternative credentialing bridges the gap between formal education and practical skills, enhancing employability through industry-recognized certifications and stackable learning units.
Nano-Degrees
Nano-degrees offer a flexible and cost-effective alternative to traditional university degrees by providing specialized, industry-relevant skills through focused, project-based learning; they enhance employability in rapidly evolving fields like technology and digital marketing. Unlike comprehensive university programs, nano-degrees enable learners to quickly acquire targeted expertise, making them ideal for career changers and professionals seeking continuous skill development.
Just-in-Time Learning
Micro-credentials offer just-in-time learning by providing targeted skills that align directly with current industry demands, enabling faster application and adaptability in professional settings. University degrees, while comprehensive, often follow longer timelines and may lack immediate relevance to evolving job requirements.
Credential Transparency
Micro-credentials offer detailed competency-based evidence that enhances credential transparency by clearly outlining specific skills and knowledge acquired, unlike traditional university degrees which often provide broader, less specified qualifications. This clarity in skill demonstration enables employers and institutions to make more informed decisions during application processes.
Modular Education
Modular education through micro-credentials offers flexible, targeted skill acquisition that aligns directly with specific application requirements, making it ideal for professionals seeking rapid competency updates. University degrees provide comprehensive theoretical foundations and broad academic exposure but may lack the agility to address evolving industry applications as efficiently as modular micro-credential programs.
University Degree vs Micro-Credential for Application. Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com