Paper application processes often lead to slower verification times and increased risk of document tampering. Blockchain credential verification offers a secure, transparent, and immutable method that accelerates the validation of applicant information. This technology reduces administrative burdens while enhancing trust and accuracy in application assessments.
Table of Comparison
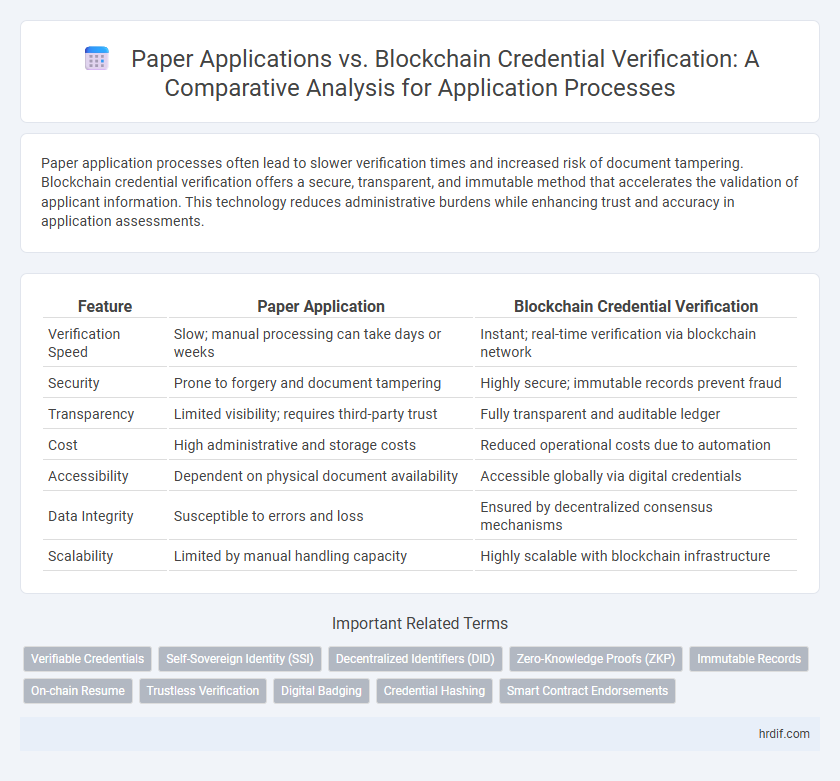
| Feature | Paper Application | Blockchain Credential Verification |
|---|---|---|
| Verification Speed | Slow; manual processing can take days or weeks | Instant; real-time verification via blockchain network |
| Security | Prone to forgery and document tampering | Highly secure; immutable records prevent fraud |
| Transparency | Limited visibility; requires third-party trust | Fully transparent and auditable ledger |
| Cost | High administrative and storage costs | Reduced operational costs due to automation |
| Accessibility | Dependent on physical document availability | Accessible globally via digital credentials |
| Data Integrity | Susceptible to errors and loss | Ensured by decentralized consensus mechanisms |
| Scalability | Limited by manual handling capacity | Highly scalable with blockchain infrastructure |
Introduction: Evolving Methods in Job Application Verification
Traditional paper application verification relies on physical documents that are prone to forgery, loss, and delays in processing. Blockchain credential verification offers a decentralized, tamper-proof solution that enables instant validation of applicant credentials through cryptographic proofs. This emerging technology enhances trust, reduces fraud, and streamlines the hiring process by providing verifiable, immutable records accessible to employers in real-time.
Paper Application Processes: Traditional Strengths and Weaknesses
Paper application processes offer familiarity and broad accessibility, allowing applicants without digital skills to participate easily. However, manual handling increases risks of errors, delays, and fraud, while verification requires significant time and resources. These limitations hinder scalability and real-time updates compared to blockchain credential verification systems.
Blockchain Credential Verification: How It Works
Blockchain credential verification streamlines the application process by securely recording and validating credentials on a decentralized ledger, eliminating the risk of forgery and reducing manual verification time. Each credential is issued as a tamper-proof digital certificate linked to the applicant's unique blockchain ID, enabling instant verification by authorized parties. This method enhances transparency, ensures data integrity, and provides applicants with full control over their verified credentials during submission.
Speed and Efficiency: Comparing Verification Timelines
Blockchain credential verification drastically reduces verification timelines by enabling instant, secure access to data, eliminating the days or weeks often required for paper application processing. Paper-based methods rely heavily on manual review and physical document transfer, contributing to delays and inefficiencies. Leveraging blockchain technology streamlines the application process, enhancing speed and reducing administrative overhead.
Data Security: Protecting Applicant Information
Paper application processes expose applicant information to risks such as loss, unauthorized access, and tampering due to physical handling and storage vulnerabilities. Blockchain credential verification enhances data security by utilizing decentralized ledgers and cryptographic encryption, ensuring immutable and transparent records accessible only to authorized parties. This technology significantly reduces fraud and protects sensitive applicant data through secure, verifiable digital identities.
Fraud Prevention: Authenticity in Application Credentials
Paper application credentials are vulnerable to forgery and manipulation, posing significant risks to fraud prevention in the application process. Blockchain credential verification enhances authenticity by providing immutable and transparent records that ensure data integrity and tamper-proof validation. This decentralized verification system reduces identity fraud and streamlines credential authentication, making it a robust solution for secure application processing.
Candidate Experience: User-Friendly Verification Processes
Blockchain credential verification significantly enhances candidate experience by offering a seamless and user-friendly process compared to traditional paper applications. Digital verification allows instant authentication of credentials without the delays and manual errors associated with physical document handling. This streamlined approach reduces candidate frustration, accelerates application timelines, and builds trust in the verification process.
Employer Benefits: Streamlining Recruitment Decisions
Blockchain credential verification enhances employer benefits by providing instant, tamper-proof validation of applicant qualifications, significantly reducing the time spent on manual paper application checks. This technology streamlines recruitment decisions with automated verification processes, minimizing human error and fraud risk. Employers gain increased confidence in candidate authenticity, leading to more efficient and secure hiring workflows.
Cost Implications: Paper vs Blockchain Verification Methods
Paper application verification incurs ongoing costs related to physical storage, manual labor, and the risk of forgery or loss, leading to inefficiencies and expenses. Blockchain credential verification minimizes verification time and reduces administrative overhead by automating identity validation through decentralized, tamper-proof digital records. The initial setup costs of blockchain systems are offset by long-term savings due to enhanced security, faster processing, and reduced fraud risk.
Future Trends: The Shift Toward Digital Credentialing
Digital credentialing is rapidly replacing paper applications due to enhanced security, real-time verification, and reduced fraud risks. Blockchain credential verification ensures immutable records and instant access, streamlining application processes across industries such as education, employment, and licensing. Future trends indicate widespread adoption of decentralized digital credentials, promoting transparency and efficiency in credential management.
Related Important Terms
Verifiable Credentials
Verifiable Credentials enable secure, tamper-proof validation of applicant information through blockchain technology, significantly reducing the risks associated with traditional paper applications such as fraud and data manipulation. Blockchain-based credential verification enhances trust and efficiency by providing decentralized, easily accessible, and cryptographically verifiable proof of qualifications and identity.
Self-Sovereign Identity (SSI)
Paper application methods lack the immutable security and instant verifiability offered by blockchain credential verification, making them vulnerable to forgery and manual errors. Self-Sovereign Identity (SSI) leverages blockchain technology to enable applicants to control their digital credentials securely, ensuring privacy, traceability, and real-time authentication during the verification process.
Decentralized Identifiers (DID)
Decentralized Identifiers (DIDs) offer a robust alternative to traditional paper applications by enabling secure, tamper-proof credential verification through blockchain technology, eliminating reliance on centralized authorities. This decentralized framework enhances privacy and interoperability, allowing applicants to maintain control over their identities while facilitating seamless, verifiable access to services.
Zero-Knowledge Proofs (ZKP)
Zero-Knowledge Proofs (ZKP) enhance blockchain credential verification by enabling users to prove the validity of their credentials without revealing sensitive information, surpassing the privacy limitations of traditional paper applications. This cryptographic method ensures secure, tamper-proof identity verification and streamlines application processes through decentralized trust mechanisms.
Immutable Records
Blockchain credential verification ensures immutable records by storing application data on decentralized ledgers, preventing tampering and enhancing data integrity. In contrast, paper applications are prone to forgery and physical damage, lacking a secure, permanent audit trail for verification purposes.
On-chain Resume
On-chain resumes leverage blockchain credential verification to provide immutable and easily accessible proof of qualifications, enhancing trust compared to traditional paper applications prone to forgery. This decentralized approach ensures real-time validation and reduces administrative overhead in the hiring process.
Trustless Verification
Blockchain credential verification enables trustless authentication by eliminating intermediaries and reducing fraud through decentralized, immutable records, whereas paper applications rely on traditional manual validation methods prone to errors and counterfeiting. This trustless system enhances security, transparency, and efficiency in verifying applicant credentials without the need for third-party involvement.
Digital Badging
Digital badging leverages blockchain credential verification to enhance application authentication, providing immutable, verifiable records compared to traditional paper applications prone to forgery and loss. Blockchain-based digital badges streamline verification processes, improve security, and enable instant validation across diverse platforms, elevating trust and efficiency in credential management.
Credential Hashing
Credential hashing in blockchain credential verification enhances security by creating a tamper-proof digital fingerprint of each applicant's credentials, unlike paper applications which rely on physical documents vulnerable to forgery. This cryptographic process ensures data integrity and enables instant verification, significantly reducing fraud and administrative delays in application processing.
Smart Contract Endorsements
Paper applications rely on manual verification processes prone to errors and delays, whereas blockchain credential verification leverages smart contract endorsements to automate and secure the validation of credentials in real-time. Smart contracts provide immutable, transparent records that enhance trust and reduce fraud in application workflows.
Paper Application vs Blockchain Credential Verification for application Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com