Adaptability empowers employees to navigate changing roles and environments seamlessly, fostering continuous growth beyond traditional linear paths. Unlike the career lattice, which emphasizes structured lateral moves and skill development within predefined frameworks, adaptability focuses on agility and resilience in response to unpredictable market demands. Embracing adaptability enhances job mobility by enabling workers to pivot quickly, seize new opportunities, and thrive amid evolving organizational needs.
Table of Comparison
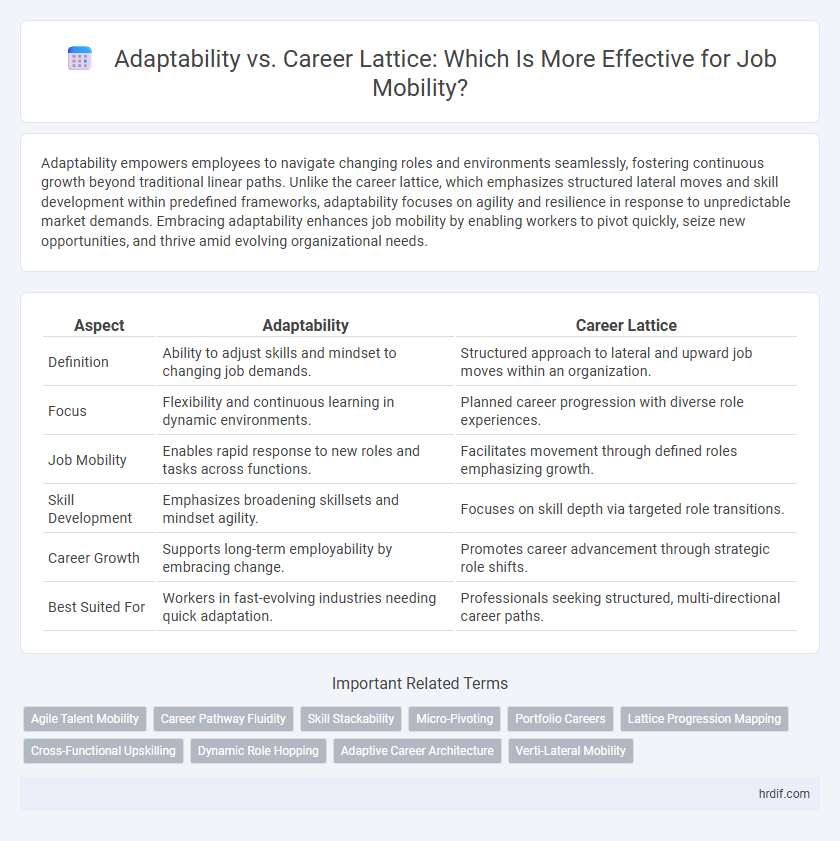
| Aspect | Adaptability | Career Lattice |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Ability to adjust skills and mindset to changing job demands. | Structured approach to lateral and upward job moves within an organization. |
| Focus | Flexibility and continuous learning in dynamic environments. | Planned career progression with diverse role experiences. |
| Job Mobility | Enables rapid response to new roles and tasks across functions. | Facilitates movement through defined roles emphasizing growth. |
| Skill Development | Emphasizes broadening skillsets and mindset agility. | Focuses on skill depth via targeted role transitions. |
| Career Growth | Supports long-term employability by embracing change. | Promotes career advancement through strategic role shifts. |
| Best Suited For | Workers in fast-evolving industries needing quick adaptation. | Professionals seeking structured, multi-directional career paths. |
Understanding Adaptability in the Modern Workplace
Understanding adaptability in the modern workplace reveals its critical role in navigating dynamic job demands and shifting organizational structures. Adaptability emphasizes continuous learning and flexibility, enabling employees to pivot across roles and responsibilities effectively. In contrast, the career lattice model highlights lateral moves and skill diversification, underscoring adaptability as the foundation for sustainable career mobility and long-term success.
What Is a Career Lattice?
A career lattice is a flexible approach to job mobility that emphasizes lateral and diagonal moves instead of only upward promotions. It allows employees to develop a diverse skill set by shifting across different roles, departments, or functions within an organization. This model supports adaptability by encouraging continuous learning and versatile career growth paths.
Adaptability vs Career Lattice: Key Differences
Adaptability emphasizes an individual's ability to adjust to new roles, skills, and environments, enabling fluid movement across different job functions. The career lattice focuses on structured, multi-directional progression within an organization, prioritizing lateral and vertical moves that build expertise. While adaptability fosters continuous learning and flexibility, the career lattice ensures strategic growth aligned with organizational goals.
The Benefits of Embracing Adaptability in Your Career
Embracing adaptability in your career accelerates job mobility by enabling you to navigate diverse roles and industries with agility. Unlike the rigid progression of a traditional career lattice, adaptability fosters continuous learning and resilience, unlocking a broader spectrum of opportunities and professional growth. This dynamic approach increases employability and positions you to thrive amidst evolving market demands and technological advancements.
How the Career Lattice Model Supports Job Mobility
The Career Lattice model supports job mobility by emphasizing lateral moves, skill diversification, and cross-functional experiences rather than traditional upward promotions. This flexible structure allows employees to adapt to changing job markets and organizational needs, enhancing their professional growth and resilience. By facilitating varied career paths, the lattice model encourages continuous learning and agility, key components of adaptability in the workforce.
Challenges in Navigating Career Lattices
Navigating career lattices presents challenges such as ambiguous role definitions and unpredictable progression paths, requiring high adaptability to manage lateral moves and skill shifts effectively. Employees must continuously update competencies and embrace flexibility to thrive within non-linear career structures. Persistent ambiguity in organizational expectations can hinder job mobility and career planning without strategic personal development.
Adaptability Skills Essential for Career Progression
Adaptability skills such as cognitive flexibility, emotional resilience, and continuous learning are essential for navigating the dynamic pathways of a career lattice. These skills enable professionals to respond to changing roles, acquire diverse competencies, and seize lateral or upward mobility opportunities. Developing adaptability accelerates career progression by fostering agility in shifting job responsibilities and evolving industry demands.
Integrating Adaptability with the Career Lattice Approach
Integrating adaptability with the career lattice approach enhances job mobility by enabling professionals to navigate both vertical promotions and lateral moves effectively. Adaptability cultivates versatile skills and openness to change, which align with the career lattice's emphasis on diverse role experiences and skill development. This synergy supports continuous growth and resilience in evolving job markets.
Real-World Examples: Adaptability and Career Lattice Success Stories
Real-world examples highlight how adaptability drives success within career lattices by enabling professionals to shift roles and industries seamlessly. Employees who embrace continuous learning and flexibility often advance faster, as seen in tech industry leaders who transition across functions from software development to product management. Career lattices that encourage lateral moves paired with adaptable skill sets foster resilience and sustained job mobility.
Future Trends in Job Mobility: Adaptability or Career Lattice?
Future trends in job mobility emphasize adaptability as a critical skill, enabling professionals to navigate evolving career lattices that prioritize diverse, non-linear progression paths. Organizations increasingly value adaptive employees who can pivot across roles and industries, aligning with dynamic market demands and technological advancements. Embracing adaptability supports continuous learning and agility, essential for thriving within complex, multi-directional career lattices.
Related Important Terms
Agile Talent Mobility
Agile talent mobility leverages adaptability by enabling employees to navigate a career lattice, moving laterally or diagonally across roles to build diverse skills and experiences. This dynamic approach contrasts with linear career paths, fostering resilience and rapid response to evolving organizational needs.
Career Pathway Fluidity
Career lattice models emphasize lateral moves and skill diversification, promoting adaptability through fluid career pathways rather than traditional upward trajectories. This approach enhances job mobility by enabling employees to pivot across roles and functions, fostering continuous growth and resilience in dynamic work environments.
Skill Stackability
Adaptability enhances job mobility by enabling skill stackability, allowing professionals to transfer and combine competencies across various roles within the career lattice framework. Skill stackability promotes continuous learning and flexible career paths, empowering individuals to navigate complex job lattices and seize diverse opportunities.
Micro-Pivoting
Micro-pivoting enhances adaptability within a career lattice by enabling professionals to make small, strategic shifts in skills and roles, facilitating continuous growth and job mobility without drastic career changes. This approach leverages incremental adjustments to navigate complex job landscapes, promoting resilience and sustained employability in dynamic industries.
Portfolio Careers
Adaptability in a portfolio career enhances job mobility by allowing professionals to leverage diverse skills across multiple roles within a career lattice framework, fostering continuous growth and flexibility. Unlike linear career paths, portfolio careers emphasize skill versatility and cross-functional experiences, enabling seamless transitions and resilience in dynamic job markets.
Lattice Progression Mapping
Lattice progression mapping enhances job mobility by visualizing diverse career paths through lateral moves and skill development, promoting adaptability in an evolving job market. This strategic approach enables employees to leverage transferable skills and embrace flexible roles, accelerating growth beyond traditional vertical promotion models.
Cross-Functional Upskilling
Cross-functional upskilling drives adaptability by enabling employees to navigate diverse roles within a career lattice, enhancing job mobility through versatile skill sets. This approach fosters continuous learning and flexibility, crucial for thriving in dynamic work environments.
Dynamic Role Hopping
Dynamic role hopping within a career lattice framework enhances job mobility by leveraging adaptability to navigate diverse skill sets and evolving responsibilities. This approach fosters continuous learning and flexibility, enabling professionals to respond swiftly to market demands and internal organizational shifts.
Adaptive Career Architecture
Adaptive Career Architecture emphasizes flexibility by allowing employees to navigate diverse roles based on evolving skills and interests rather than following a rigid Career Lattice model. This approach enhances job mobility by fostering continuous learning and leveraging individual adaptability to meet dynamic organizational needs.
Verti-Lateral Mobility
Verti-lateral mobility in career lattices emphasizes adaptability by enabling employees to move fluidly across roles that combine vertical advancements and lateral shifts, enhancing skill diversification and organizational agility. This approach fosters a dynamic workforce capable of responding to evolving job demands while accelerating professional growth beyond traditional hierarchical pathways.
Adaptability vs Career Lattice for job mobility. Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com